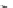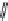Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
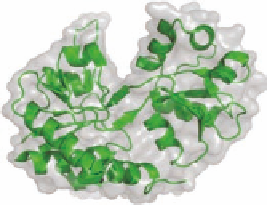
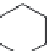
FIGURE 2.11
Structures of the ligand-binding core of the ionotropic glutamate receptor GluR2. (A) The
open, unbound form of GluR2 (pdb-code 1FTO). (B) The NeuroSearch compound NS1209 stabilizes GluR2
in the open form (pdb-code 2CMO). (C) The endogenous ligand glutamate introduces domain closure of
GluR2 by a “Venus l ytrap” mechanism (pdb-code 1FTJ). (D) Various synthetic agonists (here Br-HIBO) also
introduce domain closure in GluR2 (pdb-code 1M5C).
This design was made possible only by a detailed insight into the structure of insulin and the inter-
molecular interactions between the insulin molecules in the crystalline phase.
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas and it is responsible for the regulation of glucose
uptake and storage. Insulin is most often associated with diabetes mellitus, which is a disease caus-
ing hyperglycemia. Healthy people have a basal level of insulin in the bloodstream, but in response
to intake of food or to cover glucose clearance from the blood, peaks of larger insulin concentrations
appear throughout the 24 h of a day. Patients with diabetes may have difi culties in maintaining the
proper insulin concentrations, basal as well as peak concentrations, and accordingly regulation of
their insulin level is essential. Type I diabetes patients need insulin to supplement endogenously
produced insulin, whereas Type II diabetes patients often are getting insulin in order to improve
glycemic control.
HO
CO
2
H
Br
OH
O
N
S
O
N
N
O
H
2
N
CO
2
H
O
H
2
N
O
CO
2
H
CO
2
H
H
N
Glutamate
Br-HIBO
NS1209
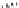
FIGURE 2.12
Chemical structures of glutamate, the agonist Br-HIBO, and the antagonist NS1209.