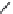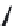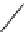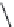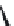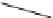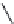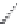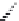Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
H
H
R
3
N
H
CH
2
C
NH
O
H
HO
N
H
H
H
OH
HN
H
H
NH
2
H
HO
H
C
NH
2
N
H
HO
O
H
H
N
NH
2
O
H
OH
H
O
HO
H
H
HOCH
2
H
O
H
H
O
H
O
H
OH
O
O
H
N
H
3
C
CH
3
NH
2
OH
C
H
O
OH
R
1
O
R
2
CH
2
H
OH
OH
HO
OH
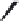
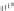
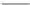
Streptomycin
Neomycin B
R
1
=
R
1
=
R
1
=
R
1
=
H
R
2
=
R
2
=
CH
2
NH
2
=
NH
2
NH
2
R
3
R
3
R
3
R
3
H
=
Neomycin C
Paromomycin I
Paromomycin II
CH
2
NH
2
R
2
=
H
CH
2
NH
2
H
=
OH
R
2
=
=
CH
2
NH
2
OH
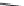
FIGURE 25.10
Streptomycin, neomycin, and paromomycin.
HO
R
2
O
R
1
R
4
HO
H
2
N
O
NH
2
HO
O
O
NH
2
HN
R
3
R
1
R
2
R
3
R
4
OH
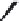
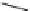
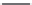
Kanamycin
OH
OH
H
Amikacin
H
OH
OH
OH
CO
C
CH
2
CH
2
NH
2
OH
Tobramycin
NH
2
H
OH
H
Dibekacin
NH
2
H
H
H
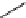
FIGURE 25.11
Kanamycin and related compounds.
gentamicins A, B, and C, from which the C component is isolated. Sisomicin was isolated in 1970
from
Micromonospora inyoensis
and netilmicin is obtained by the ethylation of sisomicin.
Another aminoglycoside that was obtained by partial synthesis is amikacin, where a l-2-hydroxy-4-
aminobutyryl group was introduced in the C1 amino group of the deoxystreptamine ring of kanamycin
(1972). The increased use of the aminoglycosides for the treatment of infections with Gram-negative
bacteria has led to the development of strains resistant to these antibiotics (Figure 25.12).