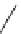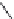Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Me
Me
Me
Me
HO
HO
Me
Me
MeCOO
OH
O
MeCOO
OH
O
OH
OH
Me
OH
OH
Me
Me
Me
MeO
Me
NH
MeO
Me
NH
O
O
CH
N
N
N
Me
O
OR
O
OR
O
O
Me
Me
R = CH
2
COOH
R = H
Rifampicin
Rifamycin B
Rifamycin SV
α-
L
CH
3
CH
3
O
H
O
C
O
CH
3
O
H
C
NH
CO
OH
CH
3
O
H
C
O
H
OH
OH
C
O
NH
2
Novobiocin
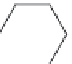
FIGURE 25.8
Rifamycins and novobiocin.
25.4.2.1 Novobiocin
Novobiocin was isolated in 1955, simultaneously in several laboratories in the United States Novobiocin
producing microorganisms were
Streptomyces niveus, S. spheroides
. Novobiocin is a coumarin
derivative. It is active against Gram-positive bacteria and also
H. inl uenzae, Neisseria
. It has been
used in the treatment of infections caused by resistant staphylococci, but numerous other products
are available now.
25.4.2.2 Quinolones
Nalidixic acid was discovered by G. Lesher et al. in the Winthrop laboratories in 1962. Its original trade
name Negram
®
indicates that it is active against Gram-negative bacteria. Subsequently some derivatives
were introduced, e.g., oxolinic acid (1967), cinoxacin (1970), norl oxacin (1978). The last product had
already a much superior activity both against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. More recent
compounds like ciprol oxacin and ol oxacin have a broad-spectrum activity (Figure 25.9).
25.5
ANTIBIOTICS AFFECTING THE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
25.5.1 I
NHIBITORS
OF
THE
30 S R
IBOSOMAL
S
UBUNIT
25.5.1.1 Aminoglycosides
Streptomycin, discovered in 1944 by Schatz, Bugie, and Waksman in
Streptomyces griseus
was the
i rst aminoglycoside. It was active mainly against Gram-negative bacteria, and for that reason it was
a useful complement to penicillin, which was active against Gram-positive bacteria. Streptomycin
together with
p
-aminosalicylic acid were the i rst drugs used in the treatment of tuberculosis.