Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
OH
O
OH
O
H
O
N
N
N
H
H
2
N
N
Methotrexate
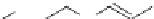
FIGURE 22.9
Structure of methotrexate, which is a structural analog of folic acid, and is used in the treat-
ment of severe autoimmune and inl ammatory diseases.
IL-6. Secondary effects of corticosteroids include the blocking of IL-2, IFN-
γ
, and tumor necro-
sis factor alpha (TNF-
). These elements, notably IL-1, are essential for lymphocyte and APC
communication. A decrease in production of these cytokines effectively obstructs an APC's
capacity to activate antigen-specii c lymphocytes. Glucocorticoids have a hydrophobic structure
that allows them to easily diffuse into cells and bind to specii c cytoplasmic receptors. The result-
ing complexes progress to the nucleus, where they are able to inhibit the transcription of the
cytokine genes. Corticosteroids are also able to inhibit cytokine production in macrophages. This
subsequently inhibits the macrophage phagocytosis and chemotaxis properties. Corticosteroids
are potent nonspecii c anti-inl ammatory agents-administration of corticosteroids results in an
acute reduction of circulating lymphocytes and monocytes.
Methotrexate (Figure 22.9), a structural analog of folic acid, is involved in the i rst line treat-
ment of severe autoimmune and inl ammatory diseases. It is classii ed as an antimetabolite drug,
which means it is capable of blocking the metabolism of cells. As a result of this effect, it is used in
treating diseases associated with abnormally rapid cell growth, such as cancer, RA, and psoriasis.
Methotrexate and its active metabolites compete for the folate binding site of the enzyme dihydro-
folate reductase (DHFR). Folic acid is reduced to tetrahydrofolic acid by DHFR for DNA synthesis
and cellular replication to occur (see Chapter 20). Competitive inhibition of the enzyme leads to
blockage of tetrahydrofolate synthesis, depletion of nucleotide precursors, and inhibition of DNA,
RNA, and protein synthesis. Methotrexate also inhibits thymidylate synthase and the transport of
reduced folates into the cell. Methotrexate is believed to diminish inl ammation by diminishing
cytokine production. It has been shown that it has direct effect on T cell function in vitro and in
vivo. Due to the nonspecii c effects on cell proliferation methotrexate treatment is accompanied by
serious side effects and more specii c alternatives are required. The new immunomodulating bio-
logics (see below) may offer alternative possibilities for less toxic treatments.
α
22.5 IMMUNOMODULATING BIOLOGICS
22.5.1 R
ECOMBINANT
P
ROTEIN
AND
E
NGINEERED
P
ROTEINS
Biologics cover peptides or proteins that are used as therapeutic modalities for medical treatment.
Immunomodulating biologics are proteins such as cytokines, interferons (IFNs), or interleukins or
it could be monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) blocking their action. It has so far not been successful to
make small molecules or peptide mimetics of the large extra cellular protein-protein interactions
through which these molecules exert their action and we therefore see a lot of new biologics com-
ing to the market in this area. Many proteins that may be used for medical treatment are normally
expressed at very low concentrations; however, through recombinant DNA technology a large quan-
tity of proteins can be produced.
Protein engineering can be used to stabilize proteins and improve in vivo half lives either by
introduction of mutations or by introducing chemical modii cations such as PEGylation, the latter