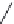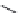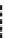Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Cl
H
3
C
NH
NH
2
Liver
N
HN
N
Cl
H
2
N
N
HN
HN
Cl
H
2
N
N
N
HN
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
C
NH
2
21.29
21.30
21.31
FIGURE 21.16
Metabolic conversion of proguanil (
21.29
) into cycloguanil (
21.30
) and coni gurations of
pyrimethamine (
21.31
).
Asp54
O
-
O
H
H
CH
3
N
+
N
Ser108
H
N
OH
CONH
2
N
Cl
H
H
RO
O
N
O
O
OH
H
H
OH
IIe14
ILe164
FIGURE 21.17
Binding of pyrimethamine (
21.31
, Figure 21.16) to the dihydrofolate binding site of dihy-
drofolate reductase (DHFR). The binding is stabilized through hydrogen bondings between the carboxylate of
Asp54 and the positively charged NH group of the 2-amino group and the nitrogen of the pyrimidine ring, of
hydrogen bonds between 4-amino group and the backbone carbonyl groups of Ile14 and Ile164. In addition,
a charge-transfer interaction between the chlorophenyl residue and the dihydropyridine ring of the NADPH
and i nally a hydrogen bond between the Ser108 and one of the hydrogen acceptors at the NADPH molecule
stabilize the complex. (
R
= the remaining part of the NADPH molecule.)
H
2
N
H
2
N
NH
2
OCH
3
N
OCH
3
S
S
O
O
N
N
O
O
21.33
21.34
FIGURE 21.18
Coni gurations of sulfadoxine (
21.33
) and dapsone (
21.34
). Compare these structures with
para
-aminobenzoic acid (
21.35
Scheme 21.4).