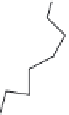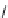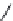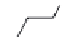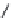Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CH
2
CH
2
R
3
R
4
2
7
6
8
S
N
H
HO
5
1
HO
R
OH
N
9
R
H
R
R
5'
6'
R
4'
S
H
H
3'
7'
8'
N
N
N
2'
1'
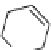
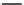
4-Quinolinemethanol
21.23
R=OCH
3
21.24
R=H
21.25
R=OCH
3
21.26
R=H
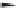
FIGURE 21.14
4-Quinoline methanols. Absolute coni gurations of (−)-quinine (
21.23
), (−)-cinchonidine
(
21.24
), (+)-quinidine (
21.25
), and (+)-cinchonine (
21.26
).
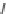
OH
H
3
C
S
HO
H
R
N
Cl
H
3
C
N
CF
3
Cl
F
3
C
CF
3
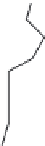
21.27
21.28
FIGURE 21.15
Absolute coni guration of (+)-mel oquine (
21.27
) and coni guration of halofantrine (
21.28
).
treatment of malaria. The narrow therapeutic window of the cinchona alkaloids in combination
with different concentrations of the alkaloids in the bark depending on species and time of harvest-
ing made access to the homogenous compounds as a major therapeutic improvement. In spite of
the several severe side effects including cardiac arrhythmia, insulin release causing hypoglycemia,
and peripheral vasodilatation the cinchona alkaloids are still used for treatment of multiresistant
malaria, most frequently in combination with tetracyclines. The treatment, however, requires care-
ful supervision.
The mechanism of action of the cinchona alkaloids is unknown, but the target might be situated
in the cytosol of the parasite. Clinically quinidine and cichonine (both 8
R
,9
S
) are two- to threefold
more active than quinine and cinchonidine (8
S
,9
R
). Quinidine and cinchonine, however, should be
used only in the case of shortage of quinine because of a narrow therapeutic window. The impor-
tance of the stereochemistry at C8 and C9 is illustrated by the lack of activity of 9-epiquinine
(8
S
,9
S
).
21.5.5.2.2 Mefl oquine
Mel oquine (
21.27
) (Figure 21.15) was selected among 300 quinolinemethanols prepared in order
to develop agents that are effective against chloroquine resistant agents. Mel oquine is marketed as
a 1:1 mixture of the two diastereomeric racemic pairs. The four stereoisomers show similar abil-
ity to inhibit hemazoin formation in vitro. The pharmacokinetic, however, is different for the two
since the half-life of the (−)-isomer (enantiomer of
21.27
) is signii cantly longer than that of the
(+)-isomer of
21.27
.
The 2,8-bis-tril uoromethyl arrangement proved to be the most active of the series. Compounds
that possessed 2-aryl groups were found to have augmented antimalarial activity, but at the same