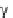Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Since all these compounds are increasing activity at the GABA
A
receptor via a positive allosteric
interaction with one common binding motif, the term agonist has been applied. It should be noted,
however, that the activity of benzodiazepines is dependent on the activation of the receptor by
GABA, the ligand that directly gates the ion channel (see Chapter 15). These compounds are best
referred to as positive allosteric modulators or BzRAs.
The GABA
A
receptor is a pentameric structure composed of i ve subunits surrounding a central
ion channel pore. The receptor subunits comprise of families of related proteins termed a1-6, b1-3,
g1-3, d, e, p, q, and r. The majority of receptors are composed of 2a, 2b, and 1g subunits. Other
subunits can substitute for g, such as, d to form a benzodiazepine insensitive subtype of receptor. The
binding site for BzRAs is located at the interface between a and g subunits in the pentameric assem-
bly of subunits (Figure 20.5). Since the g subunit of the GABA
A
receptor contains a binding motif
for a synaptic intercellular protein, g containing receptors are predominantly synaptically located.
Detailed pharmacological studies have revealed that BzRAs enhance the opening frequency
of the activated receptor, thereby allowing more current (more specii cally chloride ions) to pass
through the receptor-controlled channel within a i xed period of time. On the macroscopic level,
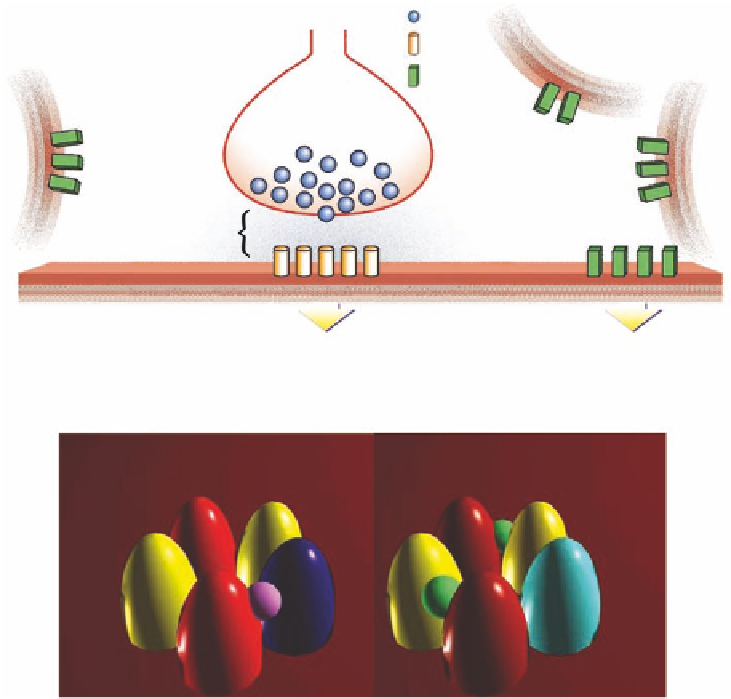
GABA-containing vesicle
Presynaptic
GABA-releasing
neuron
GABA
A
receptor
GABA
A
receptor
Synapse
Postsynaptic cell
Synaptic
inhibition
Tonic
inhibition
Synaptic
Extra synaptic
β3
α4
β3
α1
β3
β3
γ2
δ
α1
α4
FIGURE 20.5
Top: Localization of GABA
A
receptors. g containing GABA
A
receptors are predominantly
located in the synapse and determine phasic inhibition. In contrast, d containing GABA
A
receptors are located
outside the synapse (extra-synaptically) and contribute to tonic inhibition. Bottom: Synaptic and extra-synaptic
receptors are different in subunit composition and pharmacology. Whereas synaptic receptors contain the g
subunit and are sensitive to BzRAs, extra-synaptic receptors contain d (or only a and b) and are insensitive to
modulation by BzRAs. The binding site for BzRAs is located at the interface of a and g, whereas the GABA
binding site is located at the interface between a and b.