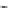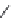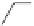Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
N
NH
2
CN
O
HN
HN
HN
N
N
HN
OUP-16
4-Methylhistamine
N
N
NH
Cl
N
N
NH
2
S
H
2
N
O
NH
VUF8430
VUF6884
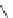
FIGURE 17.8
Histamine H
4
receptor agonists.
H
4
(40-fold) over the H
3
receptor is OUP-16 (Figure 17.8). This compound acts as a full H
4
agonist.
More recently, the potent H
4
agonist 4-methylhistamine was discovered after the screening of a large
number of histaminergic compounds. This compound was originally developed for an H
2
research
program, but appears to be more than 100-fold more potent on the H
4
receptor than on any other
histamine receptor subtype, including the H
2
receptor. VUF8430 was also reported as a potent H
4
agonist (pEC
50
= 7.3) with a complimentary selectivity proi le, being 33-fold selective over the H
3
receptor. Again, VUF8430 was originally developed as a dimaprit analog in an H
2
research program.
VUF6884 was developed as a clozapine analog with optimized histamine H
4
receptor afi nity. This
rigid compound is particularly useful for pharmacophore modeling studies (see below). Interestingly,
VUF6884 is a full agonist on histamine H
4
receptors and an even more potent histamine H
1
receptor
inverse agonist. Clozapine derivatives are well known as promiscuous GPCR ligands.
17.5.3 H
ISTAMINE
H
4
R
ECEPTOR
A
NTAGONISTS
Potent and selective H
4
receptor antagonists are also emerging. For this histamine receptor subtype,
the i rst nonimidazole ligands were found by successful HTS campaigns. The i rst reported neutral
antagonist was derived from an indole-containing hit structure that was efi ciently converted into
JNJ7777120 (Scheme 17.4). This compound can currently be considered as an H
4
receptor reference
ligand. Unfortunately, the compound has a poor stability in human and rat liver microsomes and
Cl
Cl
O
O
O
N
H
H
H
N
N
N
NH
N
N
HTS hit
K
i
= 38 nM
JNJ7777120
K
i
= 4 nM
VUF6002
K
i
= 26 nM
(A)
Cl
Cl
N
N
N
O
NH
H
H
N
Cl
N
NN
HTS hit
K
i
= 124 nM
(B)
K
i
=2 nM
SCHEME 17.4
Illustration of two histamine H
4
receptor HTS hits (A and B) and subsequent hit optimization.