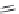Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
N
N
N
O
2
N
O
NC
O
O
H
2
NO
2
S
O
2
N
O
2
N
H
O
H
O
O
2
N
H
O
CNQX (
15.70
)
DNQX (
15.71
)
NBQX (
15.72
)
CH
3
O
OH
N
P
N
O
OH
N
O
N
O
N
N
H
O
N
COOH
HO
H
N
H
O
F
3
C
HN
O
OH
(H
3
C)
2
NO
2
S
H
NS 1209 (
15.74
)
ZK200775 (
15.73
)
LY293558 (
15.75
)
O
O
O
N
N
O
O
OH
O
O
N
N
P
HO
O
OH
H
2
N
N
O
H
2
N
H
2
N
GYKI 52466 (
15.77
)
(S)-ATPO (
15.76
)
Talampanel (
15.78
)
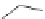
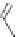
FIGURE 15.17
Structures of some competitive (
15.70
-
15.76
) and noncompetitive (
15.77
and
15.78
) AMPA
receptor antagonists.
acid and AMPA, have been found to be competitive AMPA receptor antagonists. LY293558
(
15.75
), a member of the former class, is systemically active although it shows signii cant antago-
nist effects at KA receptors in addition to its potent AMPA receptor blocking effects. The AMPA
receptor antagonist (
S
)-ATPO (
15.76
), which was designed using AMPA as a lead structure,
has like LY293558 a carbon backbone longer than that which normally confers AMPA receptor
agonism.
The 2,3-benzodiazepines, such as, GYKI 52466 (
15.77
) and Talampanel (
15.78
), represent a
class of noncompetitive AMPA receptor antagonists that have enabled the effective pharmaco-
logical separation of AMPA and KA receptor-mediated events. These compounds appear to bind
to sites distinct from the agonist recognition site, and are thus negative allosteric modulators.
Ta la mpa nel (
15.78
), currently under clinical development as a treatment for multiple sclerosis,
epilepsy, and Parkinson's disease, may inhibit AMPA receptor function even in the presence of
high levels of Glu (Figure 15.17).
15.7.7 M
ODULATORY
A
GENTS
AT
AMPA R
ECEPTORS
The agonist induced desensitization of AMPA receptors can be markedly inhibited by a number of
structurally dissimilar AMPA receptor potentiators known as AMPA-kines, including aniracetam
(
15.79
), cyclothiazide (CTZ) (
15.80
), and in particular CX-516 (
15.81
), which has been shown to
improve memory function in aged rats. These AMPA-kines positively modulate ion l ux via stabiliza-
tion of receptor subunit interface contacts and subsequent reduction in the degree of desensitization.
A series of more potent arylpropylsulfonamide-based AMPA-kines have been identii ed, including
LY395153 (
15.82
) (Figure 15.18).