Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 13.2
Ca
v
Channel Terminology and Properties
Channel Subtype
Ca
v
1
Ca
v
2
Ca
v
3
Former names
L-type
Ca
v
2.1 = P/Q type
Ca
v
2.2 = N type
Ca
v
2.3 = R type
T-type
Activation threshold
High voltage
High voltage
Low voltage
Blocker
Dihydropyridines
Phenylalkylamines
Benzothiazepines
Ca
v
2.1 blockers:
ω
-conotoxin MVIIC,
Mibefradil
R
-(−)-efonidipine
Kurtoxin
ω
-agatoxin IVA Ca
v
2.2: blockers:
ω
-conotoxin
MVIIA Ca
v
2.3 blocker: SNX-482
-conotoxin GVIA,
ω
I
II
III
IV
Outside
C
Inside
C
N
N
C
N
K
v
(A)
Na
v
,Ca
v
N
Ca
v
,α2
C
N
N
N
Outside
Inside
C
N
C
Ca
v
δ
C
C
Ca
v
γ
minK
Na
v
β
KChIP
K
v
β
(B)
Ca
v
β
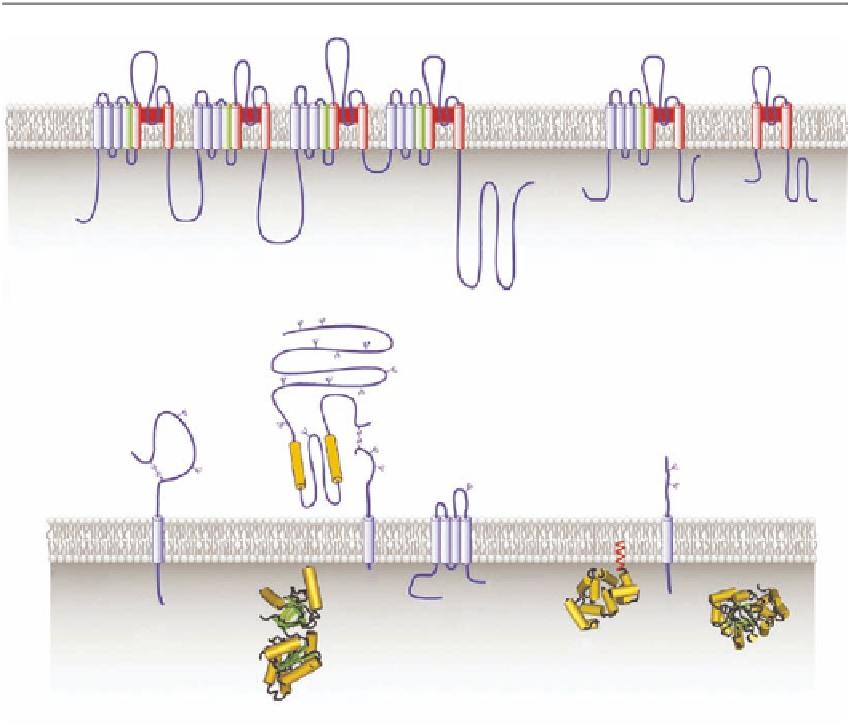
FIGURE 13.7
Overview of the membrane topology of voltage-gated ion channel α-subunits. (A) The voltage-
sensing S4 TM segments (green) contain several positively charged amino acid residues and the segments that
constitute the ion channel pore (shown in red) are the S5, S6, and pore loop segments. (B) Membrane topology
of auxiliary subunits of Na
v
, Ca
v
, and K
v
ion channels. (From Catterall, W.A. et al.,
Toxicon
, 49, 124, 2007.
With permission from Elsevier.)
α
1
-subunit, consisting of ~2000 amino acid residues.
This subunit has 24 TM segments, arranged in four linked homologous domains (I-IV), each
comprising six TM
The major component of the Ca
v
is the large
-helices (S1-S6), including the positively charged voltage-sensing S4 segments,
and the S5-S6 pore loops, with the pore loops and S6 segments believed to line the channel lumen;
the structure of the
α
α
1
- and other Ca
v
subunits is schematically shown in Figure 13.7A.