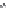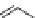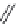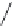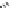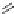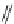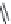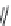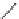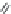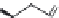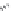Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
O
O
HO
HO
HO
O
-
O
-
O
-
H
3
C
H
3
C
H
3
C
O
OH
OH
S-CoA
NADPH
NADPH
NADP+
+ CoASH
NADP+
S-CoA
HMG-CoA
Melvaldyl-CoA
Melvalonate
O
O
O
HO
HO
HO
O
HO
O
-
O
O
OH
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
H
H
H
H
O
Compactin
Lovastatin
Simvastatin
Pravastatin
O
O
O
HO
HO
O
HO
HO
O
-
O
-
O
-
O
-
OH
OH
OH
OH
F
F
F
N
N
F
N
N
N
O
O
N
O
N
S
O
Fluvastatin
Cerivastatin
Atorvastatin
Rosuvastatin
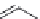
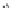
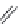
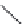
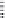
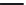
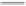
FIGURE 11.5
Structures of HMG-CoA reductase reaction substrate, tetrahedral intermediate, product, and
the statin inhibitors. Compactin, Lovastatin, and Simvastatin are type I statins. All other statins are type II
statins. The melvaldyl tetrahedral intermediate that is mimicked in all statins is shaded in gray.
through natural product screening and analoging of the natural product hits. Nevertheless, it is
quite clear that all statins share a common strategy for inhibiting their target: tetrahedral inter-
mediate state mimicry.
11.4.2.2 Inhibitors of Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) catalyzes the phosphorolysis of 6-oxypurine nucleosides
and deoxynucleosides. In humans, the PNP pathway is the only route for deoxyguanosine degrada-
tion and genetic dei ciency in this enzyme leads to profound T-cell-mediated immunosuppression.
Inhibition of PNP has applications in treating aberrant T lymphocyte activity, which is implicated
in T-cell leukemia and autoimmune diseases. The challenge to inhibitor design for PNP arises from
the abundance of the enzyme in human tissues. It has been shown that near complete inhibition
of PNP (>95%) is required for signii cant reduction in T-cell function. Structural-based inhibitor
design produced some inhibitors with
K
d
values in the nanomolar range. However, clinical evalu-
ations showed that these inhibitors did not produce sufi cient inhibition of PNP to be effective
anti-T-cell therapies. Much more potent PNP inhibitors were later designed with the aid of transi-
tion state analysis. In theory, a perfect transition state inhibitor of PNP should bind with a
K
d
value
of approximately 10
−17
M (10 attomolar). The structure of the transition state for human PNP was
determined by Schramm and coworkers by measuring kinetic isotope effects. Their studies revealed
a transition state with signii cant ribooxycarbenium character (Figure 11.6). Based on the features
of this transition state, compounds with picomolar afi nity to PNP were synthesized. Among them,