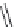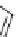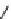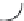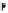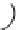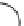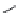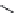Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
N
NH
CH
3
χ
1
NH
2
χ
2
CO
2
H
χ
2
χ
1
CO
2
H
CH
3
H
3
C
CH
3
CH
3
HO
NH
2
NH
2
χ
2
CO
2
H
CO
2
H
χ
2
χ
1
χ
1
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
HO
NH
2
NH
2
CO
2
H
CO
2
H
χ
1
χ
21
χ
1
χ
21
χ
22
CH
3
H
3
C
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
C
N
NH
2
R
NH
2
CO
2
H
N
CO
2
H
χ
1
χ
2
χ
1
χ
2
CH
3
R = H, CH
3
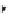
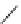
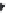
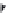
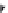
χ-Constrained amino acids synthesized in the Hruby group. (From Kazmierski, W.M. et al.,
J. Org. Chem
. 22, 231, 1994; Boteju, L. et al.,
Tetrahedron
50, 2391, 1994; Xiang, L. et al.,
Tetrahedron
, 6, 83,
1995; Qian, X. et al.,
Tetrahedron
, 51, 1033, 1995; Liao, S. and Hruby, V.J.,
Tetrahedron L ett
., 37, 1563, 1993;
Han, Y. et al.,
Tetrahedron L ett
., 38, 5135, 1997; Wang, S. et al.,
Tetrahedron L ett
., 41, 1307, 2000; Qiu, W. et al.,
Tetrahedron
, 56, 2577, 2000.)
FIGURE 8.4
The modii cation to the peptide backbone can also serve to introduce local backbone
constraints. For example, N-alkylation restricts the
torsional angle but eliminates the
hydrogen bonding capability of the amide bond.
N
-Methyl amino acids have been incor-
porated into bioactive mimetics of opioid peptides, bradykinin, thyrotropin releasing hor-
mone (THR), angiotensin II, and cholecystokinin (CCK), and many others.
φ
α
-Methyl (and
-anyl) substituted amino acids often can induce or stabilize particular turn and
helical structures.
(4)
Globally constrained peptide conformation
. Cyclization of a peptide is another general
approach to constrain the conformation by limiting the l exibility of the peptide. In this
approach, the amino acid side chain groups and backbone moieties that are unimportant in
biological activity are chosen as the sites to construct a cyclic structure. The cyclization can
be formed between side chains through different types of bonds, such as disuli des, lactams,
and thioethers (Figure 8.6). Other kinds of cyclic constraint are also possible between side
chains and C- or N-termini or between side chain and backbone nitrogens (Figure. 8.7).
By making an appropriate covalent bond between two groups one can stabilize a particular
conformer and get a relatively rigid structure that adopts a particular secondary structure.
α
-alkyl or
α