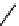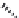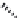Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
O
OAc
OAc
OH
O
O
O
O
H
H
XylO
XylO
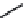
Actein
23-
epi
-26-Deoxyactein
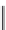
H
O
O
OH
H
OH
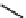
AraO
Cimigenol 3-
O
-α-
L
-arabinoside
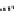
FIGURE 6.2
Some common triterpenoid constituents of black cohosh.
plant preparations marked a turning point for pharmaceutical discovery. Quinine continues to have
practical use in the treatment of certain resistant forms of
P. falciperum
.
In Chinese traditional medicine
Artemisia annua
or qinghao, has been employed as an anti-
malarial agent for many centuries. In this case, the sesquiterpene lactone artemisinin (Figure 6.1),
containing a rare peroxide bridge, was isolated from the plant material and shown to possess
effective antimalarial activity. Owing to the development of resistance to synthetic antimalarial
drugs, artemisinin has become an effective alternative therapy. The yield of artemisinin in
A. annua
is relatively low making its commercial production an expensive process. Considering that the
majority of people suffering from malaria live in underdeveloped regions of the world, a practi-
cal and cost-effective method for the production of artemisinin is highly desirable. This situation
is a prime example of what has become known as the “supply issue” for the practical production
of natural products. The issue is focused on the difi culty of producing commercial quantities of
complex natural products.
Herba l remed ies continue to play a sign ii cant role in human medicine. Chemical investigations
have identii ed many of the active principles in many commonly used products. These products
are often sold as dietary supplements rather than ethical pharmaceutical products. Because these
products are complex mixtures of many natural products there is a need to establish criteria
for their standardization. This situation is complicated by the natural variation in secondary
metabolites produced by closely related species of medicinal plants. Owing to the possibility
that variations in the composition of the products will result in unpredictable potency, the herbal
products industry has been developing quality control standards. Black cohosh, for example,
which is taken for the relief of menopausal symptoms, has a number of signature triterpenoid con-
stituents including, actein, 23-
epi
-26-deoxyactein, and cimigenol-3-
O
-arabinoside (Figure 6.2).
These compounds can be identii ed by coupled high-performance liquid chromatography-mass
spectrometry (HPLC/MS), in comparison with authentic reference compounds. Our ability to
quantify the amount of the key constituents in these herbal products will facilitate a better under-
standing of their efi cacy and permit greater coni dence in their use in medicine.
6.3 ANTIBIOTICS
The development of antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial infections, which was critical during
the war years of the early 1940s, changed the course of drug discovery efforts in the pharmaceutical
industry. Following the pioneering experiments of Selman Waksman at Rutgers University on soil
actinomycetes, pharmaceutical companies began the systematic evaluation of antibiotics produced
by bacteria isolated from the soil. During the succeeding quarter century, often referred to as the