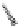
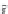
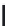
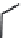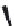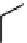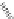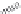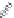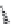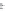Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
H
HO
N
N
HO
S
H
O
N
O
H
3
CO
H
O
NCH
3
OH
O
N
HO
Morphine
Quinine
Penicillin G
OH
OH
HO
O
O
H
2
N
OH
O
HO
O
O
Cl
O
O
Camphor
Menthol
H
H
HO
OH
Cl
O
O
O
H
N
N
H
H
HN
O
H
H
O
H
H
H
H
O
O
HN
H
H
2
N
O
HOOC
O
O
O
NH
O
OH
Vancomycin
OH
OH
HO
O
H
OH
HO
O
O
O
O
CH
3
H
Taxol
O
O
O
H
3
C
O
H
H
H
O
CH
3
O
O
Artemisinin
N
HO
HO
OH
OH
HO
Me
Cl
NMe
2
O
O
O
H
H
OH
O
O
O
CONH
2
OH
OH
OH
O
OH
O
O
Erythromycin A
(a macrolide antibiotic)
Chlortetracycline
(a tetracycline antibiotic)
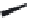
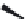
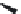
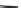
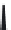
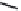
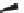
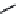
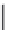
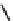
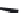
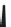
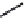
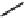
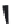
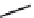
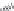
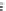
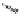
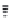
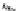
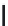
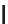
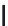
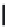
FIGURE 6.1
Examples from the major classes of natural products.
originally described as basic compounds found predominantly in plants. Alkaloids have var-
ied biosynthetic origins, frequently based on an amino acid core; the unifying structural aspect
remains the existence of a basic nitrogen function. Examples of well-known alkaloids that have
been used in medicine are morphine (from the opium poppy,
Papaver somniferum
) and quinine
(from
Chincona
species).