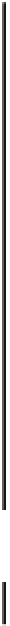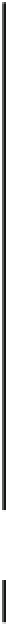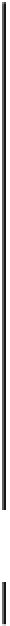Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
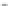
Success probability of fault injection
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
LR binary
RL binary
LR binary
with dummy
non
CRT
-based
RL binary
with dummy
Montgomery
Square-mulltiply
exponentiation
LR binary
RL binary
LR binary
with dummy
CRT
-based
RL binary
with dummy
Montgomery
Square-mulltiply
exponentiation
8.0
8.2
8.4
8.6
8.8
9.0
T
g
(ns)
ECC
6.6
6.8
7.0
7.2
7.4
7.6
T
g
(ns)
Fig. 18.9
Probability of fault injection for public cryptography. LR (RL) binary refers to the left-
to-right (right-to-left) binary method
The important thing to note is that the fault can be injected with probability 1.0
when the glitch width
T
g
is small enough, e.g.
T
g
<
8
.
0 ns for both the CRT-based
and the nonCRT-based RSA modules and
T
g
<
.
0 ns for the ECC module. The key
retrieval procedure will be discussed in Sects.
18.5.2
and
18.5.3
, respectively, for all
the CRT-based RSA modules and the dummy-operation-based nonCRT-based RSA
models.
7
18.5 Key Retrievals Using Faulty Ciphertexts
In order to verify the various attack methods of the theoretical fault analysis, we
perform the key retrieval from a faulty ciphertext obtained in our experiments. As
examples, we show the results of key retrievals using well-known fault analyses on
AES and RSA.