Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABL E 4.3. Binding Kinetics for Motavizumab Glycoforms to
Human FcRn
Sample
SPR Binding (K
d
) to Human FcRn (
m
M)
Motavizumab
2.26
G0 enriched
2.77
G2 enriched
2.18
demonstrates that the carbohydrate moiety of palivizumab is not required for virus neu-
tralization activity.
The serum levels of IgGmolecules invivo are regulated primarily through binding of
Fc portion of the antibody to FcRn receptor [19]. For this reason, we considered whether
variation in glycoforms could affect FcRn binding to motavizumab. Binding kinetics for
different glycoforms of motavizumab to human FcRnwere analyzed by SPR, as shown in
Table 4.3. The results show similar binding kinetics for motavizumab, G0-enriched, and
G2-enriched motavizumab. Because the different glycoforms have similar binding to
human FcRn, variation in glycosylation would not be expected to have an impact on PK.
N
ONCLINICAL
S
TUDIES
. The cotton rat has been the primary animal model for in vivo
testing of RSV infection and disease [20, 21]. The cotton rat model has been used to
demonstrate that passive immunization with anti-RSV antibodies can prevent RSV
infection in vivo, and these results have supported the successful clinical testing and
licensure of anti-RSVantibody prophylactics [22, 23]. For these reasons, the cotton rat
model was used for testing the impact of glycoforms on motavizumab and palivizumab
in vivo activities.
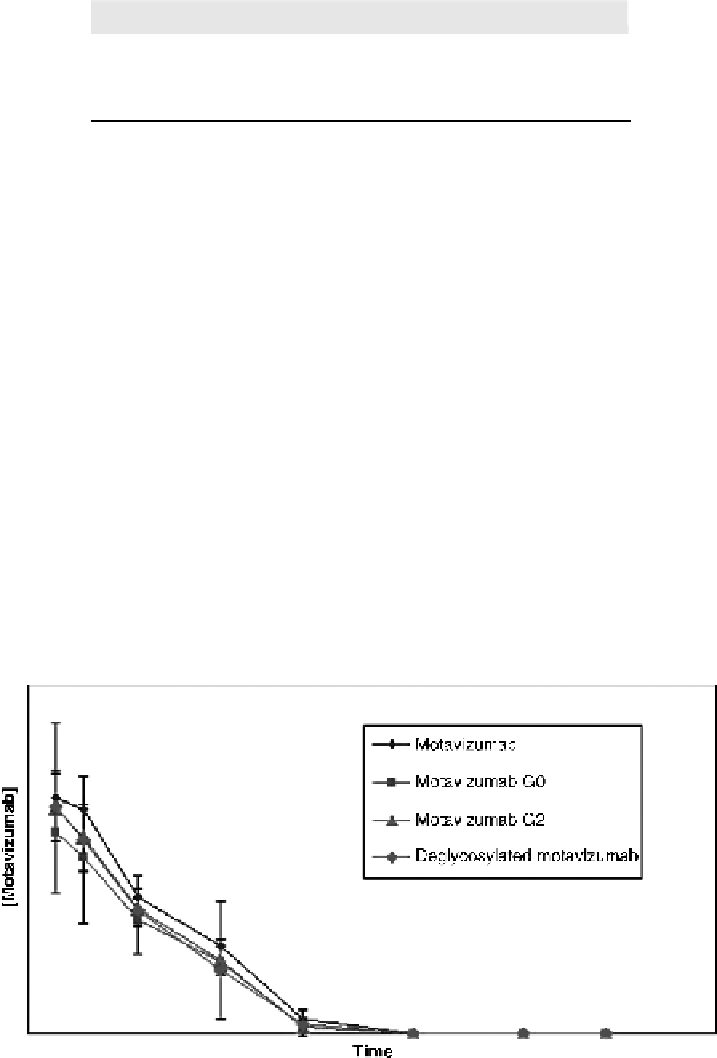
Motavizumab glycoforms and deglycosylated motavizumab were evaluated in a
cotton rat PK study. Motavizumab levels were measured in serum (Fig. 4.8), bronchial
alveolar lavage (BAL) (Fig. 4.9), and lung homogenate (Fig. 4.10). The results show that
Figure
4.8.
Cotton rat PK study: serum levels of motavizumab variants. (See the insert for color
representation of this figure.)