Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
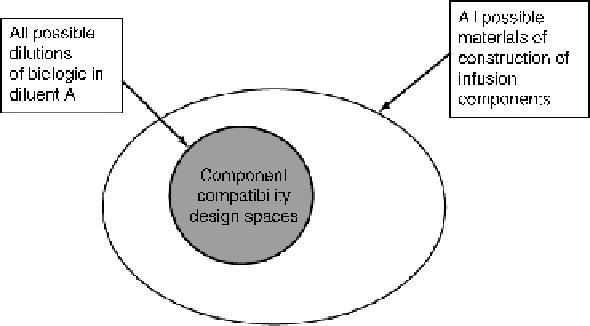
Figure
10.9.
A schematic illustration of the component compatibility design space for an
infusion product.
An important component of the above compatibility requirement is the qualification
of various infusion components for use with the biologic product. For a product to be
marketed worldwide, it is obvious that a large number of component manufacturers
would be in question. Since it is not possible to qualify all potential components for a
variety of manufacturers, a bracketing strategy based on DOE was applied. The strategy
based on qualifying materials of construction instead of specific components makes the
results applicable to components other than those tested. The elements tested in the DOE
are listed in Table 10.7, along with the actual design in Fig. 10.8.
The study showed the compatibility of the biologic with the materials of
construction of the most commonly used infusion components and the concentration
range within which the compatibility existed, thus defining a design space in which
the biologic could be used. This is illustrated schematically in Fig. 10.9.
10.4 CONCLUSIONS
A systematic work process has been defined to apply risk-based approaches to generate
process understanding and align ICHQ8, Q9, and Q10. The examples provided illustrate
the many ways in which the concepts of QbD and design space can be applied to biologic
product—formulation and process development.
REFERENCES
[1] Carpenter JF, Pikal MJ, Chang BS, Randolph TW. Rational design of stable lyophilized
protein formulations: some practical advice. Pharm Res 1997;14:969-975.
[2] Patro SY, Freund E, Chang BS. Protein formulation and fill-finish operations. Biotechnol
Ann Rev 2002;8:55-84.