Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure
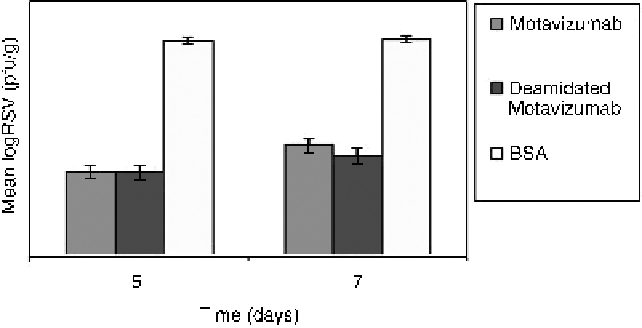
4.25. IM prophylaxis in cotton rats by deamidated motavizumab.
Deamidated motavizumab was also evaluated as a prophylaxis for RSV infection
in cotton rats. Rats were dosed with deamidated motavizumab (4 weeks at pH 8.5),
motavizumab, or BSA as a control. One group was challenged with RSVon Day 1 and
thesecondonDay3postdosingwththerespective protein. Four days post
challenging, all rats were sacrificed and lung RSV titers were measured. Both
deamidated and nondeamidated motavizumab provided 2.5 logs of RSV clearance
when assessed at 5 and 7 days postdosing (Fig. 4.25). Serum and lung levels of
motavizumab and deamidated motavizumab were measured on the day the animals
were sacrificed and levels were found to be similar. These data indicate that
deamidated motavizumab remains potent in an in vivo model, is effective in binding
to the RSV, and the antibody remains in both serum and lungs at concentrations
necessary for viral neutralization.
Although deamidation in the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) may
affect antigen binding, no deamidation sites are present in themotavizumab CDRs. There
are no known literature reports of immunogenicity in monoclonal antibodies linked to
deamidation. The impact of deamidation on immunogenicity was evaluated in nonclini-
cal and clinical studies. Cynomolgus monkeys were administered doses sixfold higher
than the clinical dose at weekly intervals for 6months and were thus exposed to far higher
levels of deamidated product than would occur with the typical five monthly clinical
doses. No immunogenicity or adverse reactions were observed.
N
ONCLINICAL AND
C
LINICAL
S
TUDIES
—P
ALIVIZUMAB
. Similar to the results for mota-
vizumab, palivizumab purified from clinical PK samples showed an increase in acidic
isoforms indicative of deamidation (Fig. 4.26). Extensive studies were performed to
verify that deamidated palivizumab retains biological activity. These studies showed that
both normal and buffer-deamidated palivizumab retain biological activity as determined
by the primary potency assay (F protein binding ELISA, 109 and 113% relative potency,
respectively), as well as the relevant in vitro (RSV microneutralization, Fig. 4.27) and
in vivo (cotton rat PK and cotton rat challenge) bioassays (Figs 4.28 and 4.29).