Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
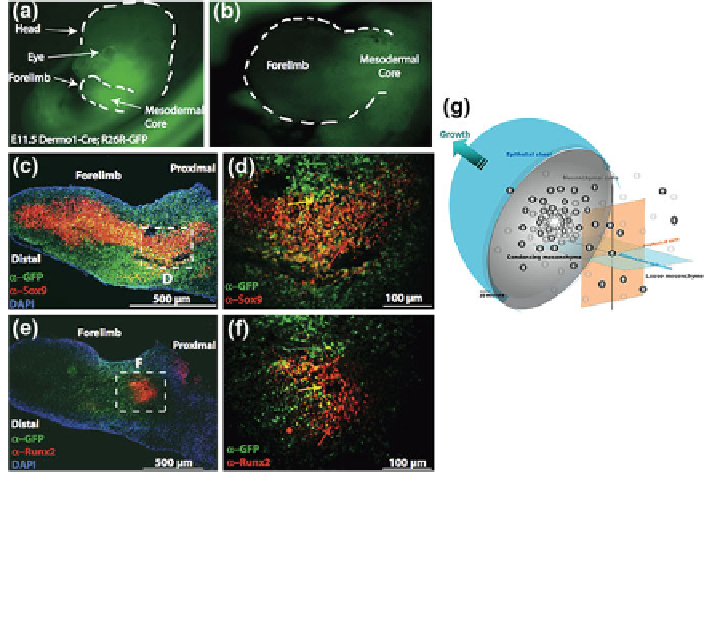
Fig. 4 Key extrinsic factors and their role in mesenchymal condensation, the first step of
skeletogenesis. (a, b) The embryonic murine limbud is shown at E11.5, where the mesenchyme is
bulbous in shape. Although possessing the same genetic code, lineage commitment by each cell is
highly dependent on spatiotemporal signals including deviatoric and dilatational stress states as
well as the biochemical milieu. For example, the expression of Sox9, a genetic marker of
chondrogenesis (c, enlarged in d) is spatially distinct from that of Runx2, a genetic marker of
osteogenesis (e, enlarged in f). Adapted from [
27
], used with permission
for exploitation of tissue scaffolds as delivery devices for exogenous and
endogenous cues, including biochemical and mechanical signals, to drive the fate
of MSC seeded within [
27
].
Recent studies demonstrate the promise of delivering spatiotemporally con-
trolled mechanical cues to guide stem cell proliferation patterns [
2
,
14
,
25
] and
lineage commitment [
2
-
5
,
12
,
24
-
26
,
34
,
35
,
46
], essentially harnessing nature's
approach to engineering tissues. Moreover, embryonic MSC exhibit 1000-fold
greater mechanosensitivity than terminally differentiated cells (Fig.
5
)[
2
,
12
,
34
,
35
,
46
]. Already half a century ago, Pauwels postulated that dilatational stresses
such as hydrostatic or normal stresses cause differentiation of stem cells to
chondrogenic lineage whereas deviatoric or shear stress guides stem cells toward
ligamentous and tendonous phenotypes [
37
]. In vitro studies have shown that such
mechanical loading significantly affected terminally differentiated cells as well as
lineage commitment in undifferentiated multipotent stem cells [
8
,
11
,
14
,
15
,
22
,
42
,
43
]. Specifically, shear forces by fluid flow have been shown to affect baseline
gene expression of Collagen type I, II, Runx2 and Sox 9, which are markers of
mesenchymal condensation [
12
,
34
,
35
,
37
,
46
] (Fig.
6
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search