Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(8)
Take the TEM for shape and size analysis. Place one drop of aqueous dis-
persion over a 400-mesh carbon-coated copper grid followed by negative
staining with phosphotungstic acid (3%, w/v, adjusted to pH 4.7 with KOH)
and place at the accelerating voltage of 80 kV.
(9)
Record the mean hydrodynamic diameter, polydispersity and zeta potential
of core by photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS) using Zeta Nano ZS 90
(Malvern, UK) after appropriate dilution (1:200) with PBS pH 7.4 prior to
analysis.
Aquasomes are prepared using tin oxide, hydroxyapatite (HA), diamond and
brushite (calcium phosphate dihydrate).
145-147
Hydroxyapatite is biodegradable,
inexpensive, stable, and safe. It is used for tissue engineering, implants, as well
as for drug and antigen delivery
148-159
and particularly useful for protein deliv-
ery because of high adsorption capability.
160
HA particles prepared following the above process were smaller in size and
crystalline in nature.
111
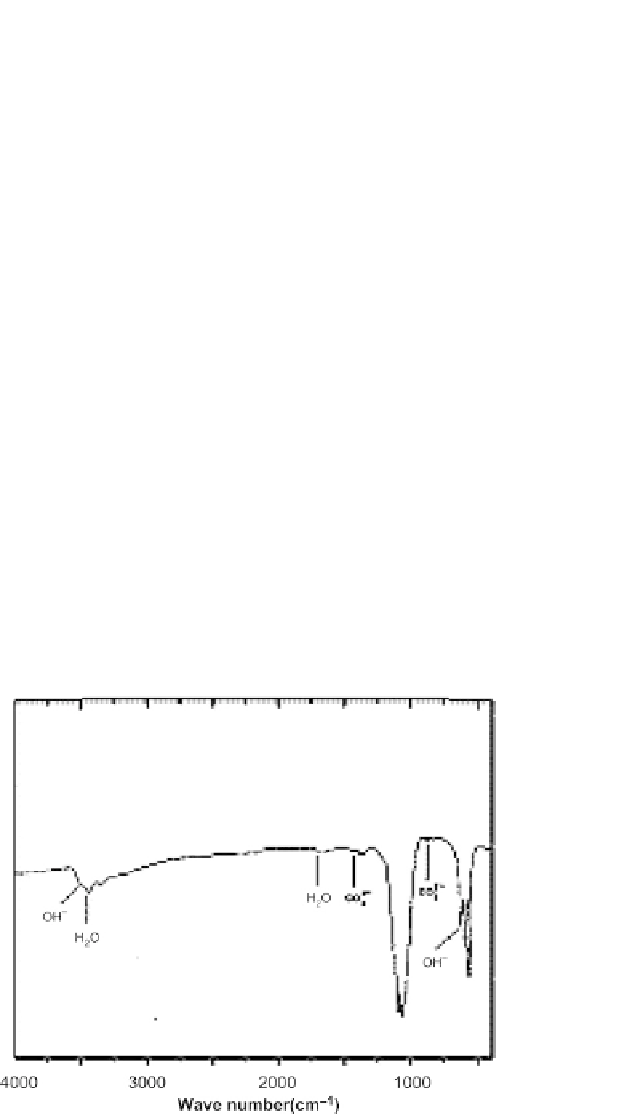
The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
bands for
PO
−
4
of the calcined powder were observed at 507, 604, 945,
964, 1024, and 1184 cm
−1
, whereas the medium sharp peak at 633, 2910, and
3570 cm
−1
was due to the OH
−1
bending deformation (
Figure 7.3
).
111
The X-ray diffraction patterns of HA showed characteristic intense absorp-
tion peaks at 31-32, 49-50, 25-27 (2θ angle) which are indicative of the crys-
talline behavior (
Figure 7.4
).
111
The ultrafine nanosize spherical morphology of
the HA core is shown in the TEM image. The DLS results supported the TEM
data with 39 nm particle diameter having a polydispersity index of 0.28.
111
FIGURE 7.3
The FTIR spectra of hydroxyapatite core particles obtained from the mixture of
calcium nitrate and di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate.
From Pandey 2011.