Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
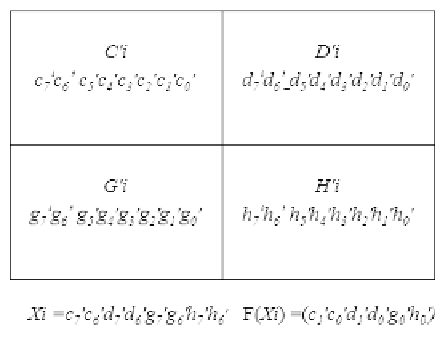
FIGURE 16.26
The bits of Xi
i
and F(X
i
) carried in the stego block.
If m
0
stego-images have passed authentication in Step 3, and
m
0
k , then continue. For each collected stego-image SI
0
i
, SI
0
i
= SI
i
; otherwise, stop the program and report failure of the se-
cret recovery step.
Step 4:
For each z =1, 2, ..., Z, Z = b
H
6
c, perform the following sub-
steps to recover the secret data P
z
.
Step 5:
(a) For each SI
0
i
,i 2f1; 2;:::m
0
g , extract the 2 most signicant
bits (MSBs) of the four pixels of each cover as the value Xi
i
specified in Equation 16.16, X = (c
0
7
c
0
6
d
0
7
d
0
6
g
0
7
g
0
6
h
0
7
h
0
6
)
D
; ex-
tract the data bits of F(Xi)
i
) from the LSBs of pixels C
0
i
, D
0
i
,
G
0
i
, and H
0
i
, as shown in Figure 16.26, as a value of F(Xi)
i
)
appearing in Equation 16.16.
(b) By using the scheme described in
Section 16.3.5,
compute
the corresponding value of y as the value P
z
.
(c) For each z = 1, 2, ..., Z, Z = b
H
6
c, perform last steps to
obtain all of the P
z
for the blocks of halftone image HI of
the secret image GI.
Step 6:
Apply the edge- and LUT-based inverse halftoning algorithm
(ELUT, introduced in
Section 16.3.4)
to the halftone image HI







Search WWH ::

Custom Search