Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
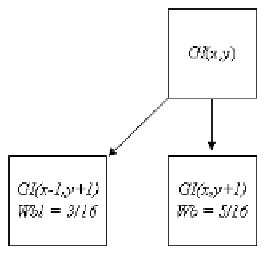
FIGURE 16.13
The neighboring pixels that accepted error diffusion for Case 3.
16.3.2 Interpolation Technique
In computer computations, a discrete number system rather than a real num-
ber system is applied due to the limitations of machine representation. There-
fore, a continuous signal must be sampled for computer storage and calcula-
tion. However, sampling is always destructive to the original information and
new samples often must be reselected when the sampling scale is changed. Let
us denote R as a real signal performed in the real number system as shown
in Figure 16.14(a); denote D as the digital signal created by R, which is per-
formed in the discrete number system shown in Figure 16.14 (b). The digital
signal D
0
shown in Figure 16.14(c) is generated by sampling digital signal D.
FIGURE 16.14
Example of sampling an image: (a) Real signal R; (b) Sampled signal D of R;
(c) Sampled signal D' of D.
Figure 16.14 shows that the re-sampled signal D
0
can be easily retrieved
when the real signal R is always available. However, the original signal is
usually discarded after receiving the digital signal D. As a result, the resampled








Search WWH ::

Custom Search