Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
6
7
8
1
9
0
8
2
10
5
0
10
12
4
14
6
4
3
2
13
11
3
11
1
9
15
14
12
15
7
13
5
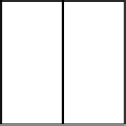
FIGURE 4.5
Samples of ordered dither matrices. Clustered-dot matrix (left) and dispersed-
dot matrix (right).
Density Pattern
It is obvious to achieve (l + 1) gray levels, i.e., tones, with l binary pixels.
The density pattern method uses l subpixels for representing each pixel value.
This is similar to the visual cryptography in the sense that a resulting image
requires more pixels than the original image. If we adopt this type of halfton-
ing method, the resulting shadow images and reconstructed secret image are
lm times larger than the original continuous-tone images. Of course, this is
inappropriate since people want to make a resulting image as small as possible.
Noise-Encoding
The easiest way to obtain a binary image from a continuous-tone image of the
same size is thresholding, which assigns 0 to a pixel of the resulting binary im-
age if the original pixel value is smaller than a threshold value. Otherwise it as-
signs 1 to the binary pixel. However, the resulting binary image usually suffers
from pseudo-contours. Noise-encoding is a key concept for improving image
quality. In the early stage of digital halftoning studies, random noise, i.e., white
noise, is used for this purpose. A binary image obtained by adding random
noise followed by thresholding yields better quality than a simply-thresholded
image, because it reduces pseudo-contours. Random dither is a simple exten-
sion of noise-encoding. It uses a random threshold array and thresholds each
pixel with a random number instead of using a constant threshold after adding
a random number to the pixel value.
Ordered Dither
Noises need not be random and a threshold matrix can be generated with a
certain order. Ordered dither generates a binary image by comparing a pixel
of an original continuous-tone image with a threshold value of the periodic
ordered matrix. The methods based on ordered dither are classified into two
categories, clustered-dot ordered dither, and dispersed-dot ordered dither de-
pending on the nature of generated dots.
Clustered-dot ordered dither turns adjacent pixels on which form a cluster
in the matrix. The period length of dots is determined by that of the matrix.
The tone level of a region is modulated by the area size of clustered-dot. Thus,
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search