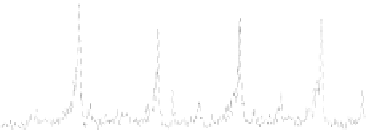Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
FCR
0.2
0.15
ECR
0.1
0.05
0
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
t s
60
40
20
0
-20
-40
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
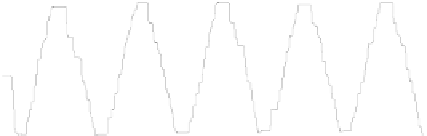
Figure 5.3
A representation of the EMG envelopes of the FCR (doted line), ECR (solid
line) muscles, and their overlap (thick solid line) in a tracking trial (upper panel) and the
tracking trajectory (lower panel) represented by the actual wrist angle (solid line) and the
target angle (dashed line). For color reference, see page 215.
5.3 EVALUATION ON TRAINING EFFECTIVENESS
For evaluation of the effectiveness of the developed continuous intention-driven
robot on the wrist joint, we conducted a randomized controlled trial (RCT), which
quantitatively compared the training effects of the developed robot with those
achieved in a robot-assisted CPM training. After obtaining approval from the
Human Subjects Ethics Sub-Committee of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University,
we screened voluntarily enrolled persons after stroke coming from local districts.
Subjects recruited satisfied the inclusion criteria: 1) had unilateral ischemic brain
injury or intracerebral hemorrhage at least 6 months after the onset of single
stroke; 2) had moderate level of motor impairment in the affected upper limb,
assessed by FMA (9
18); 3) Subjects had to
be able to follow the training procedures. Randomization was done by computer-
generated random numbers for different groups (i.e., the interactive group and
the passive group), assigned according to the order of the recruitment. The study
utilized a multiple baseline design, assessed by the clinical scores of the FMA
(shoulder/elbow and wrist/hand), and the MAS (wrist and elbow). Each outcome
was measured 3 times in two weeks before the training. A total of 86 hemiplegic
subjects were screened for the training. Twenty-seven of them met the selection
criteria and were recruited for this study. After the randomization, the subjects
were divided into the interactive group (n
<
shoulder/elbow
<
27, 6
<
wrist/hand
<
=
15) and the passive group (n
=
12).
5.3.1 Interventions
The subjects received a wrist treatment consisting of 20 sessions, with a training
intensity of at least 3 sessions and at most 5 sessions a week. All training sessions