Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(1983); Jefferson; (1990)). We have termed this the “lateral system” (Saitoh; (1996)).
With the lateral system, the positional gap between the anatomical and orthotic
hip joints is small and the motion of the orthosis during the gait is similar to a
anatomical motion.
On other hand, in the RGO, the hard pelvic support that links the hip joints is
not rigid enough to achieve good stability during standing and walking. The very
rigid pelvic band in the HGO greatly restricts trunk movement. In addition, the
structure of these orthoses, i.e., lateral-sided hip joints and hard pelvic support,
makes it difficult to use a wheelchair while wearing them.
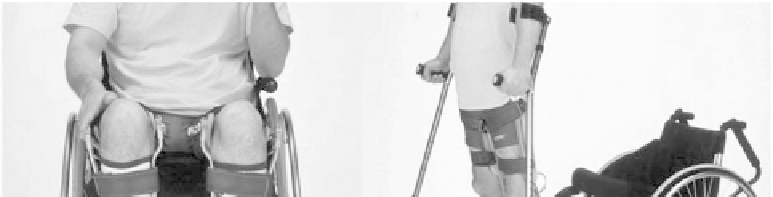
To address these issues, a new unique system, which we call the “medial
system”, has become available in medical practice. It is characterized by a medial
single hip joint located between the thighs of KAFOs under the perineum (Saitoh;
(1996), Saitoh; (1997)).The medial system, introduced as the Walkabout in 1992,
had excellent standing stability and wheelchair compatibility. However, there was
a height gap in the position between the orthotic hip joint and the anatomical hip
joint, as well as the problem of a short stride in walking. Therefore, Primewalk,
which has a sliding hip joint with a virtual axis to reduce th
e
height gap problem,
was developed and put into use (Saitoh; (1997), Suzuki; (2007)).The Primewalk
Figure 3.3
Primewalk System. For color reference, see page 212.