Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
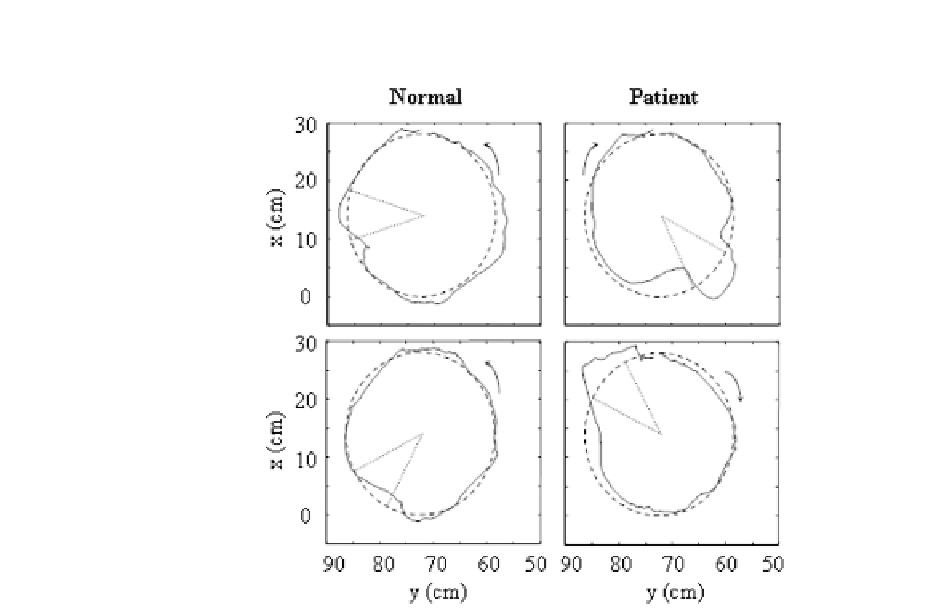
Figure 9.4
Random perturbation as a test of control capability in a normal subject and a
stroke patient.
9.3 EVALUATION OF BENEFITS FOR REHABILITATION WITH
ROBOTS
The main manifestations of motor deficits in stroke patients include weakness,
loss of dexterity, spasticity and abnormal synergy. In clinical practice, MRC
scale (Bates, 1995), Brunnstrom's Stage (BrS) (Brunnstrom, 1970), the FuglMeyer
assessment (FM) (Fugl-Meyer
et al.
, 1975), the Functional Independence Measure
(FIM) (Tinetti, 1986), and the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS)(Bohannon and
Smith, 1987) are used to semi-quantify motor deficits and functional capability.
Although these clinical indices reflect motor deficits they are ordinal and heavily
depend on the judgment of raters.
Many robotic systems have relevant parameters for quantification of treatment
efficacy Gerachshenko
et al.
, 2008; Schwerin
et al.
, 2008; Sakatani
et al.
, 2007). These
parameters may originate form kinematics, kinetics and electromyogram (EMG).
Usually, the efficacy of robot system in rehabilitation is reported with results from
scale evaluation and quantitative parameters. FM and FIM are by far the most used
scale parameters. The pioneering MIT-Manus (Kwakkel
et al.
, 2008; Wolbrecht
et al.
, 2008) showed a beneficial effect of robot-assisted upper limb treatment of
severely affected stroke patients. MIME system (Rosati
et al.
, 2007; Hesse
et al.
,
2005) has been validated for chronic patients that could provide the affected limb
to perform a mirror movement of the movement defined by the intact limb. Arm