Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
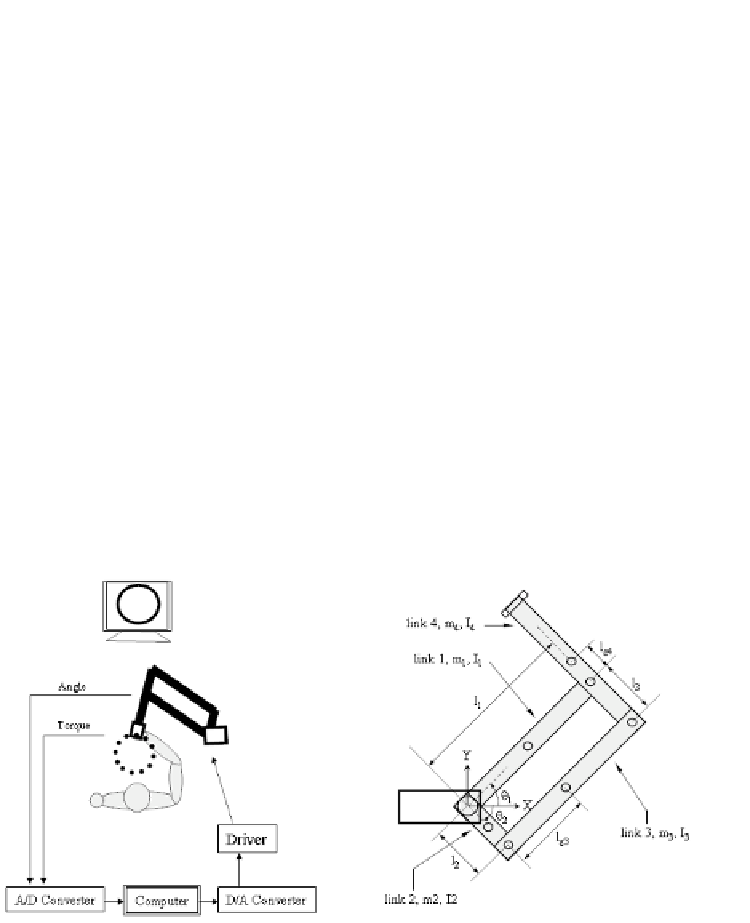
Figure 9.1
Upper: a photo of our planar robot for rehabilitation of the upper limbs, lower
left: the components of the robot and lower right: the five-bar-link drive mechanism.
b
f
˙
when
˙
·
θ
k
+
τ
c
θ
k
>
0
τ
fk
=
(9.4)
˙
when
˙
·
θ
k
−
τ
θ
k
<
=
b
f
0
k
1, 2
c
where
τ
f
1
and
τ
f
2
are torques to be compensated, b
f
is a constant for viscous
friction term and
τ
c
is a static Coulomb friction torque (Phillips and Ballou, 1993).
b
f
τ
c
are determined empirically (Lu
et al.
, 1993). For the overall control
scheme, we adopt the hybrid position/force control,
6
i.e., controlling force in the
tangential direction of the movement and controlling position in the orthogonal
direction. The main goal of control is to keep the hand of the subject in a predefined
track and to impose an assistant or resistant force along the moving direction.
and