Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
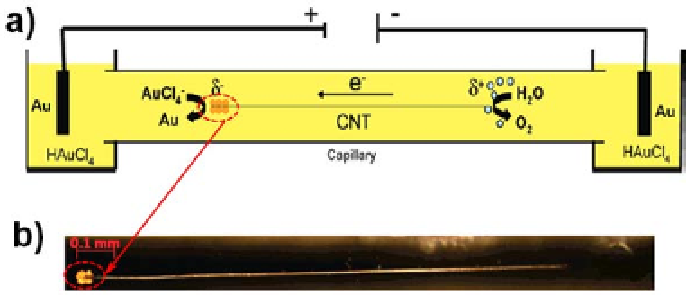
into a glass capillary connected to two reservoirs filled with HAuCl
4
electrolyte. The fiber was observed under the microscope during the
application of different potential values. It was found that potentials
higher than 40 V are needed to generate a visible metal deposit on the
cathodic side of the fiber. After less than 5 min, a visible gold deposit
was clearly formed on the negativel polarized end of the fiber. In
the course of 1 h, the metal continued growing and its morphology,
as revealed by SEM, was dominated by an agglomeration of small
crystallites. The Au particle formed after 45 min was illustrated in
Fig. 1.
21
.
Figure 1.
21
suspension
dipping in the two reservoirs of a capillary electrophoresis setup. A
high electric field is applied, leading to the polarization of the individual
nanotubes, thus triggering different electrochemical reactions on either
end. Optical micrographs of a carbon fiber inside a glass capillary during
dissymmetric gold deposition by bipolar electrochemistry. (b) The applied
voltage was 70 V for a capillary with a length of 10 cm, filled with 10 mM
HAuCl
(a) Capillary filled with an aqueous CNT/AuCl
4
aqueous electrolyte [226]. Reproduced by kind permission from
the publisher.
4
Looking to the future, this capillary-assisted bipolar
electrodeposition can be generalized to other types of nano-objects
and also deposits of a very different nature such as other metals,
semiconductors, or polymers. The approach, therefore, opens up
the way to a whole new family of experiments leading to complex
nano-objects with an increasingly sophisticated design allowing
original applications.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search