Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
also be electropolymerized by such template methods [205]. Highly
ordered magnetic nano-scale dot arrays of Ni can be fabricated from
double-templated electrodeposition [206,207]. Patterns of ordered
arrays of spheres with controlled spacing can be electrochemical
deposited by two steps. The double templates were firstly prepared
by self-assembly of PS latex spheres on a gold coated glass substrate.
This primary template was used for the electrodeposition of the
conducting polymer resulting in a macroporous polymer template.
After the deposition of PPy, the PS spheres were dissolved in toluene
leaving a secondary polymer template. The PPy was then converted
into an insulator either by over-oxidation or by undoping at a
sufficiently negative potential. This insulating structure was used
as the template for electrochemical deposition of magnetic material
such as Ni. Electrodeposition of magnetic materials gradually fills
the spherical cavities of the PPy template. Ordered arrays of Ni dots
with quasi-spherical geometry can be fabricated by this way and the
diameter of the dots can be set from 20 nm [207].
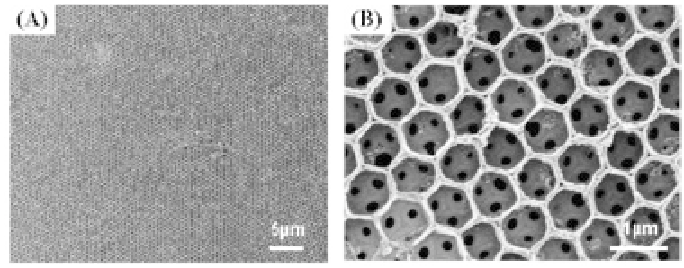
Figure 1.
19
SEM images of PANI inverse opals prepared via cyclic
voltammetry, at low (A) and higher (B) magnification. Scan rate 20 mV/s,
10 scan cycles [208]. Reproduced by kind permission from the publisher.
Ordered 3D arrays of polyaniline (PANI) inverse opals can also
fabricated via electrochemical methods by using colloidal crystals
of polystyrene beads as sacrificial templates as shown in Fig. 1.
19
[208]. Compared with films obtained by chemical synthesis, the
inverse opaline samples obtained by electrochemistry had a much
higher structural quality. Such PANI inverse opals were prepared
by a galvanostatic method at a current density 0.05 mA/cm
. By
adjusting the polymerization time and applied current, this method
2








Search WWH ::

Custom Search