Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where
Q
is the circulated charge (C cm
−2
),
M
the molecular weight of
the oxide (79.9 g mol
−1
),
F
the Faraday constant (96500 C equiv
−1
),
n
δ
the number of electrons involved in the reaction, and
the density
of TiO
). Therefore, the theoretical thickness of the
nanotube layers should be 3500 nm for 20 min of anodization,
leading to an anodization efficiency of about 20%. This relative low
value can be explained by the competition between Eqs. 1.1 and 1.2
shown in Section 5.3.2, i.e., between growth and dissolution of the
nanotube layer [26].
(3.8-4.1 g cm
−3
2
*
*
(a)
(b)
*
Titanium
+
Anatase
*
Anatase
*
Titanium
+
*
*
*
*
*
*
+
*
+
*
*
*
+
+
*
*
*
450ºC
4
50ºC
as-prepared
as-prepared
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
2 Theta / degree
2 Theta / degree
(c)
^
^
Silicon
+ Titanium
*
Anatase
+
*
+
*
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
2 Theta / degree
Figure 5.9
nanotube
layers on Ti foils with 600 nm length. (b) As-prepared and annealed ntTiO
XRD patterns of (a) As-prepared and annealed ntTiO
2
2
nanotube layers on Ti foils with 900 nm length. (c) As-prepared and after
heat treatment at 450°C of TiO
nanotube layers onto Si substrate. Note that
reflections of anatase are written in the figure.
2

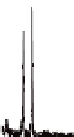




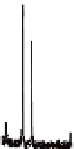





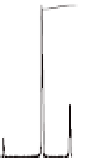


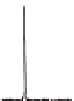







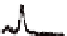



























































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search