Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
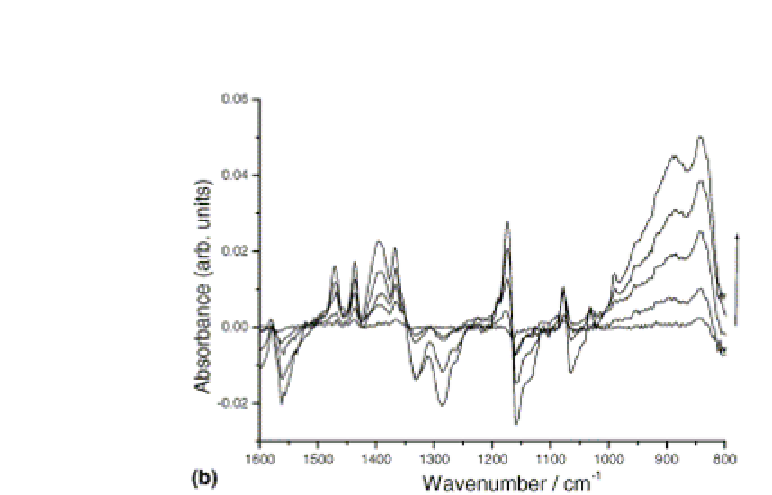
Figure 3.3
Changes in the
in situ
FTIR-ATR spectra obtained in the
wavenumber range 1600-700 cm
during electropolymerization of 0.1M
EDOT in the ionic liquid [BMIM][BF
−1
]. Potential cycling was performed
between -0.95 and +1.3 V using a 50 mV/s scan rate. IR spectra were
recorded at the end of each scan at about −0.95 V. Reprinted from
J. Electroanal. Chem.,
4
570
, Damlin, P., Kvarnström, C., and Ivaska, A.,
Electrochemical
spectroelectrochemical
characterization of poly(3,4 ethylenedioxythiophene)(PEDOT) in room
temperature ionic liquids, 113-122, Copyright (2004), with permission
from Elsevier.
synthesis
and
in
situ
N] in
polymerization of PTh [61]. They studied polymerization of three
different monomers: thiophene, bithiophene, and terthiophene. All
the three monomers were polymerized both in [EMIM][Tf
Pringle
et
al.
used
[EMIM][Tf
N]
and
[BMP][Tf
2
2
N] and
2
in [BMP][Tf
N]. The polymers showed enhanced electrochemical
activity. The polymer made in [BMP][Tf
2
N] had, however, a smoother
surface than the polymers electrosynthesized in the imidazolium-
based IL. The polymer growth rate was faster in [EMIM][Tf
2
N] since
2
it is less viscous than [BMP][Tf
N] and was explained by faster
reaction kinetics at the electrode. The type of the monomer also
influenced the structure of the final PTh. It was observed that with
increasing monomer size the relative conjugation length as well as
the impact of the IL on the electropolymerization process decreased.
2







Search WWH ::

Custom Search