Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
A
B
1.2
GFP
autofluorescence
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
Emission wavelength (nm)
GFP::DGAT-2
C
D
Merge
Autofluorescence
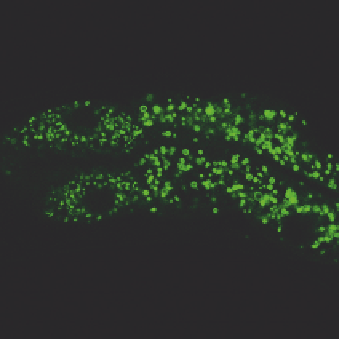
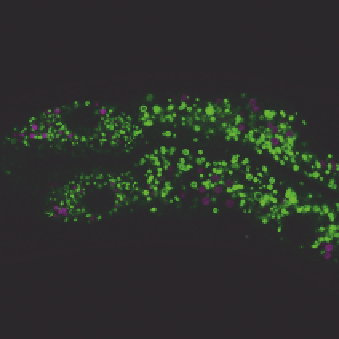
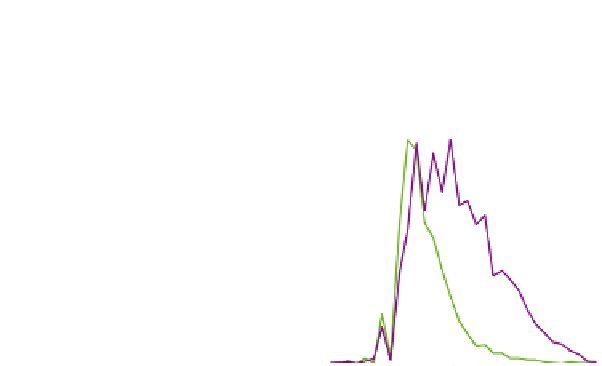
FIGURE 3.2
Visualization of GFP::DGAT-2 by laser scanning confocal microscopy. A young adult animal
was imaged and the anterior intestine is shown. (A) Reference spectra of green fluorescent
protein (GFP) (green) and autofluorescence (magenta) used for linear unmixing. (B) GFP
signals after linear unmixing. (C) Autofluorescence signals (pseudocolored magenta) after
linear unmixing. (D) Merge of (B) and (C) showing clear spatial separation of GFP and
autofluorescent signals. Scale bar, 10
m
m.
3.2.3
Discussion
Since the autofluorescent signals are confined in LROs, additional control experi-
ments can be performed in mutant animals that lack LROs. Loss of GLO-1/Rab
GTPase, GLO-2/Pallidin, GLO-3, or GLO-4/guanine nucleotide exchange factor
blocks LRO biogenesis but has no apparent effect on lipid droplets (
Hermann
et al., 2005, 2012; Rabbitts et al., 2008; Schroeder et al., 2007; Zhang, Trimble,
et al., 2010
). In principle, GFP::DGAT-2 will mark lipid droplets in
glo-1, 2, 3,