Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
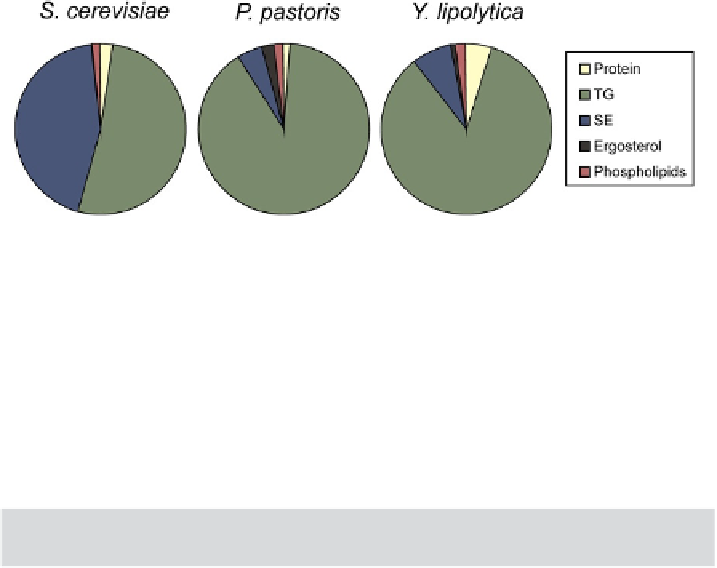
FIGURE 2.4
Major components of LD from S. cerevisiae, P. pastoris, and Y. lipolytica. Data were obtained
from
Athenstaedt et al. (2006)
,
Ivashov et al. (2012)
, and
Leber et al. (1994)
. Relative
amounts of TG (triacylglycerols), SE (steryl esters), ergosterol, phospholipids, and protein
were calculated according to analytical data.
Table 2.1
Analyses of LD Isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris,
and Yarrowia lipolytica (
Athenstaedt et al., 2006; Ivashov et al., 2012; Leber et al.,
1994
)
S. cerevisiae
(
m
g/
m
g protein)
P. pastoris
(
m
g/
m
g protein)
Y. lipolytica
(
m
g/
m
g protein)
Protein
1
1
1
TG
19.8
59.1
16.6
SE
17.2
3.1
1.53
Ergosterol
0.1
1.6
0.12
Phospholipids
0.5
1.09
0.4
Yeast strains were grown to the stationary phase on glucose media and individual components were
analyzed as described in
Section 2
. SE, steryl ester; TG, triacylglycerols.
Noteworthily, LD from
S. cerevisiae
,
P. pastoris
,and
Y. lipolytica
exhibit further
differences in their lipid profiles. First, the sterol composition from yeast LD can vary
significantly. Sterol analysis of
S. cerevisiae
LD revealed that
75% of total SE are
formed from ergosterol, whereas only minor amounts of zymosterol, fecosterol, and
episterol esters were found (
Czabany et al., 2008
). In contrast, SE from
P. pastoris
contain only 30% ergosterol esters, but larger amounts of esterified sterol precursors
(
Ivashov et al., 2012
). The amount of zymosterol in SE from
P. pastoris
is similar to
ergosterol (26%), and also substantial amounts of episterol, 4-methylzymosterol,
fecosterol, lanosterol, and 4,14-dimethylcholesta-8,24-dienol were detected. The
phospholipid pattern of LD from
S. cerevisiae
and
P. pastoris
is rather similar. Phos-
phatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylinositol are the most
abundant phospholipids forming the surface phospholipid monolayer of LD in both