Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Trypsin
Time (min)
-
++
20
10
20
130
100
70
55
40
35
25
15
10
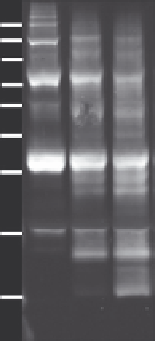
FIGURE 11.8
Limited trypsin digestion of FIT2 in 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-phosphocholine (POPC)
proteoliposomes. POPC proteoliposomes containing FIT2 were generated as described
herein and subjected to limited trypsin digestion assays described in detail elsewhere (
Gross
et al., 2010
). Briefly, intact proteosomes were incubated with or without trypsin for 10 or
20 min, then extracted with Buffer E, subjected to electrophoresis on 15% SDS-PAGE, and
subjected to western blot with anti-LL2 FIT2 antibody, which binds a luminal loop of FIT2.
Limited trypsin digestion patterns of FIT2 in proteoliposomes closely resembled those of FIT2
in digitonin-permeabilized cells (
Gross et al., 2010
).
were prepared as indicated above and subjected to limited trypsin digestion (de-
scribed in (
Gross et al., 2010
)) in the presence of Buffer A, and trypsin (Sigma)
for various times. Reactions were quenched with soybean trypsin inhibitor (Sigma)
and analyzed by immunoblot using FIT2 LL2 antibody (
Fig. 11.8
). Reconstituted
proteoliposomes generated similar limited trypsin digestion profiles as native pro-
teins digested from intact ER membranes, producing
25 kDa and
14 kDa proteo-
lytic products (
Gross et al., 2010
).
CONCLUSION AND APPLICATIONS
Many integral membrane proteins and membrane-associated proteins have been
implicated in the process of LD formation and maintenance; however, the mecha-
nism by which LDs are formed is poorly understood. It stands to reason that many
of these proteins that result in LD accumulation or depletion are either regulated by
or bind to various lipids, which may modulate their structure and/or function. In order
to understand how lipids modulate integral membrane protein behavior, a practical