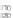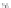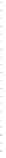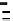Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Isolation of
LDs
Precipitation
of LD proteins
Gel slicing
Sliced gel
Digestion
MS protein identification
RT:
0.00 - 90.00
62.10
NL:
8.36E7
TIC MS 48
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
63.24
64.11
28.75
29.37
28.34
38.46
31.87
41.94
61.76
27.79
44.47
55.84
61.47
68.31
71.99
22.43
76.96
3.27
6.52
15.10
87.28
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Time (min)
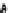
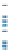
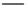
FIGURE 1.3
Proteomic analysis of isolated LDs. The schematic diagram indicates the process of LD
protein extraction, separation, gel slicing, digestion, and MS protein identification. Following
verification of the purity of the isolated LDs by biochemical and morphological examinations,
proteins are precipitated from LDs using chloroform and acetone, then separated by
SDS-PAGE, and stained. Further, the gel is sliced according to protein bands present and
subjected to an in-gel digestion. An example is from the bacterium RHA 1 in which the gel is
sliced into 43 pieces. Alternatively, total precipitated proteins are digested directly. After
digestion, the small peptides are separated and subjected to the mass spectrometer for
further analysis. The silver stained SDS-PAGE is reproduced from
Ding et al. (2012)
.
5.2.1
GFP fusion with target protein is constructed.
5.2.2
The construct is transfected into the model organism.
5.2.3
LD location of the target proteins is examined using confocal
microscopy. If the GFP signal formed a ring structure on the
surface of the LDs, this protein is a LD protein.
5.3
Western blot, comparative proteomics, and photobleaching are used to
determine protein on and off LDs.
5.3.1
LD, TM, Cyto, and PNS are collected from samples under
different biological conditions and the proteins determined
using Western blot. Distribution of target proteins represents
their dynamic movement.
5.3.2
LDs are isolated from samples under different biological
conditions and LD proteins determined using protein staining.
Altered protein bands are sliced and subjected to identification
by MS.
5.3.3
Fluorescence of the GFP-fused target protein is photobleached
from LDs and the fluorescent signal recovery determined.
5.4
A functional assay is used to examine the effects of LD proteins on LD
formation, size change, and lipolysis. The depletion and overexpression
of the identified LD proteins in the correspondence organisms are
used to determine whether the target proteins affect homeostasis and
functions of LDs.