Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
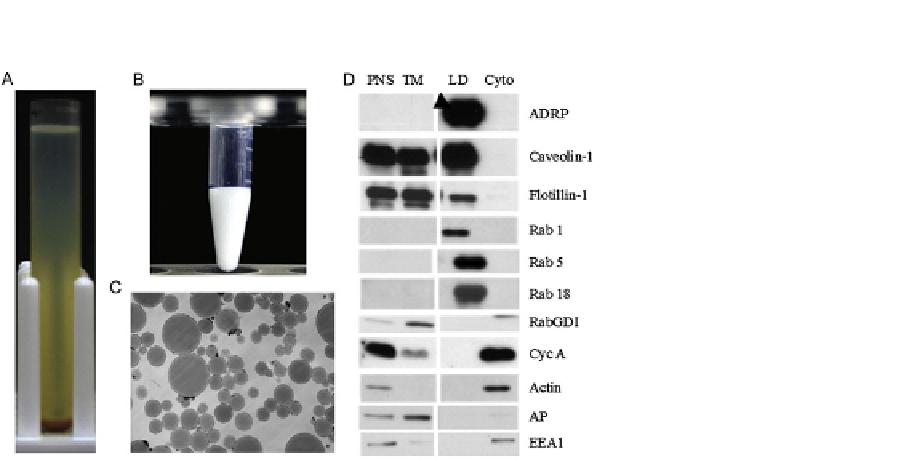
FIGURE 1.2
Quality control of isolated LDs. (A) Wild-type C. elegans worms are harvested, washed, and
homogenized. The PNS is centrifuged at 12,628
g for 1 h at 4
C. The top light layer is
the LD fraction. (B) Yeast LDs are isolated according to methods discussed. LD suspension in
an Eppendorf tube appears as a milk-like consistency. (C) Purified LDs from CHO K2
cells are fixed, dehydrated, stained, embedded, sectioned, and examined by electron
microscopy. (D) Equal amount of proteins of PNS, TM, LD, Cyto from CHO K2 cells are
separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and blotted with indicated
antibodies. Among them, ADRP is a marker protein of LDs; cyclophilin A (Cyc A), and actin
are represented cytosol; caveolin-1 and alkaline phosphatase (AP) are used as markers of
plasma membrane, and EEA1 is utilized to monitor early endosome.
(B) is reproduced from
Ding et al. (2013)
. (D) is reproduced from
Bartz, Zehmer, et al. (2007)
.
cellular fractions such as TM (total membrane), Cyto, and PNS
(
Fig. 1.1
A-C).
2.5
Morphological analysis
Isolated LDs are examined by light microscopy and electron microscopy
(
Fig. 1.2
C).
2.6
Other membrane or Cyto contaminations
To determine contamination from Cyto and other membrane structures,
protein markers of plasma membrane, ER, mitochondria, lysosome, endosome,
nuclear membrane, and Cyto are examined by Western blotting (
Fig. 1.2
D).
Step 3
Preparation of protein samples for LC-MS/MS analysis
3.1
LD proteins are separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Colloid blue,
and the gel is sliced according to protein bands.
3.2
The sliced gel pieces or total LD proteins are mixed with 10 mM DTT
by incubating at 56
C for 1 h.