Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
accounting of erosion and deposition using the
concept of 'layers' of sediment with a 'well mixed'
distribution of sediment sizes. The difference be-
tween the quantities of sediment arriving at and
leaving a computational cross-section is simply
represented as amass balance calculation based on
the Exner equation:
Features of the model include:
.
use of the iSIS interface for model preparation,
simulation and display of results;
.
coupled simulation with a fully hydrodynamic
model;
.
user may specify different bed compositions at
every cross-section and a different gradation for
the inflow of sediment;
.
looped, branched and tidal channels may be
modelled.
Limitations include:
.
the need to edit the sediment file in a text format;
.
sediment transport calculations are based on
composite cross-sectional properties;
.
a restricted set of iSIS units can be used exclud-
ing, for example, interpolated sections and fixed
roughness formulation based on Manning's n.
W
d
z
t
þ
q
G
q
ð
1
lÞ
x
¼
0
ð
5
:
5
Þ
q
where
l¼
bed porosity; W
¼
water surface width
(m); z
¼
bed elevation (m); t
¼
time (s); G
¼
sedi-
ment transport rate (m
3
/s); and x
¼
distance in
flow direction (m).
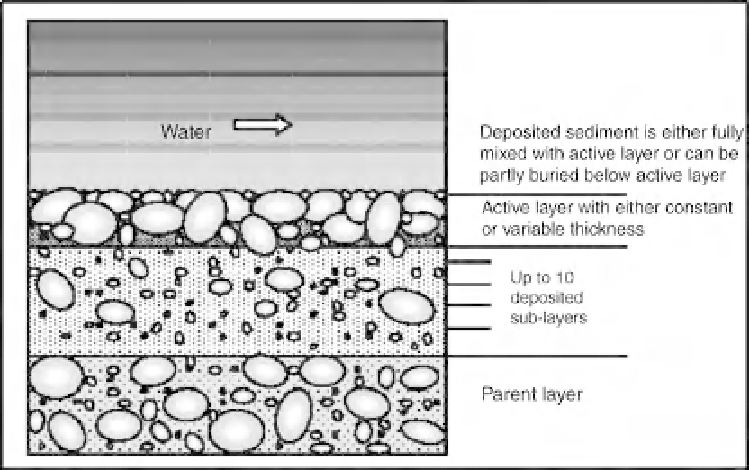
The bed layer concept (Fig. 5.12) is used to
account for sorting between active and parent
layers that is especially important in gravel-bed
rivers, where there is a wide grading of sediment,
and surface layers may be significantly coarser
than the parent material. Bank material is not
specified separately, and so is implicitly assumed
to be of the same composition as the bed material,
which is seldom the case in an alluvial stream,
especially in gravel and cobble-bed rivers.
In the standard version of iSIS the sediment
transport equations available are Engelund and
Conceptual basis
It is not necessary to recount the detailed basis for
iSIS Sediment as the computational framework
used in the hydraulic and sediment transport cal-
culations is well documented in the user manual
(iSIS 1999). The sediment simulation is based on
calculation of sediment transport rates and an
Fig. 5.12
Bed Layer Concept used in iSIS (2001).