Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
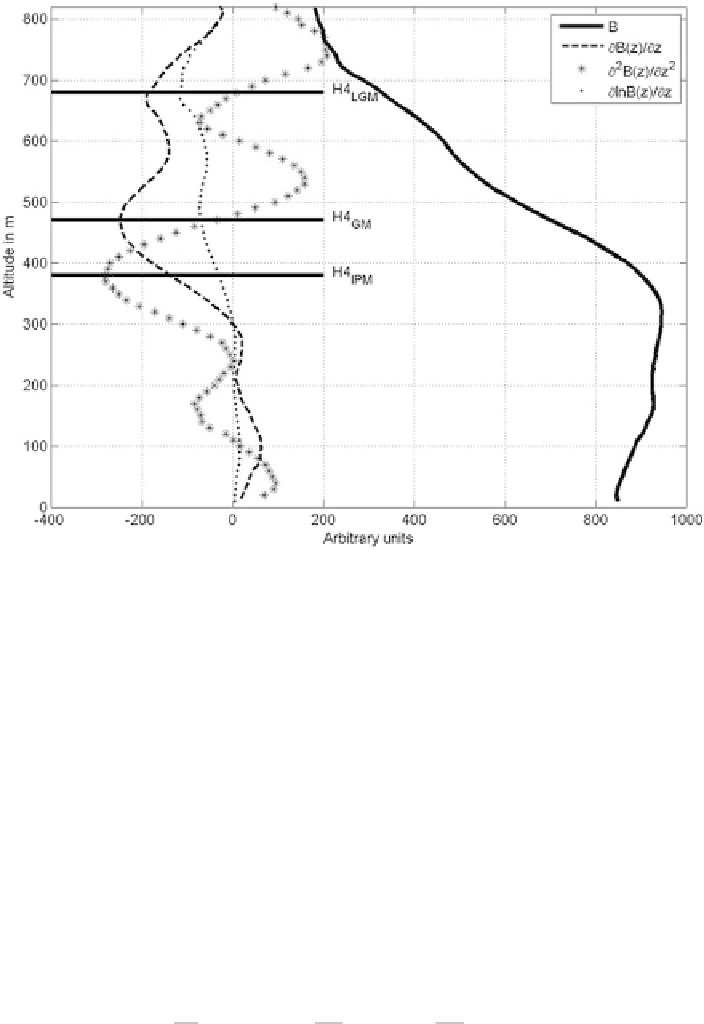
Fig. 4.4
Schematic of the determination of MLH from optical sounding.
Full black curve
: opti-
cal backscatter intensity
B
in dB,
dashed line
: vertical derivative of
B
,
asterisks
: vertical second
derivative of
B
,
dots
: vertical derivative of the logarithm of
B
.
Horizontal bars
indicate mixing
layer heights from eqs. (
4.5
)to(
4.7
). From: Emeis et al. (
2008
)
is done over 15 min and a height interval
Δ
h
of 80m. In the layer between 500 and
2000 m,
h
for vertical averaging is extended to 160 m. Two additional parame-
ters have been introduced to further reduce the number of false hits. The minimum
accepted attenuated backscatter intensity
B
min
right below a lifted inversion is set
to 200
10
−
9
m
−
1
sr
−
1
10
−
9
m
−
1
sr
−
1
×
in the lower layer and 250
×
in the upper
layer. Additionally, the vertical gradient value
∂
B
/∂
z
max
of a lifted inversion must
10
−
9
m
−
2
sr
−
1
in the lower layer and more negative
be more negative than
−
0.30
×
10
−
9
m
−
2
sr
−
1
in the upper layer.
If
B
(
z
) denotes the measured attenuated backscatter intensity in the height
z
above
ground averaged over time and height and
than
−
0.60
×
Δ
h
is the height averaging interval, then
∂
/∂
the gradient
B
z
in the height
z
is calculated as
z
=
B
(
z
)
∂
B
∂
+
h
2
−
h
2
)
−
B
(
z
/
h
,
(4.8)
z
A gradient minimum is characterized by a change of sign from minus to plus
of the second derivative of
B
(
z
). The height interval under examination is searched
from bottom to top for these gradient minima
H
4
_n
.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search