Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
In the examples presented in this section, the modeling techniques are explored us-
ing the SUrrogate MOdeling (SUMO) Matlab Toolbox [7]. SUMO is a plug in-based,
adaptive platform that can be customized flexibly. The toolbox makes it feasible to
test a variety of modeling techniques. Transient circuit simulators, including Cadence
Virtuoso Spectre
®
, and Synopsys HSPICE
®
, are used here for performing transistor-
level circuit simulations.
2.3
Circuit Case Demonstration
Performance models are very helpful for visualizing the design space and gaining
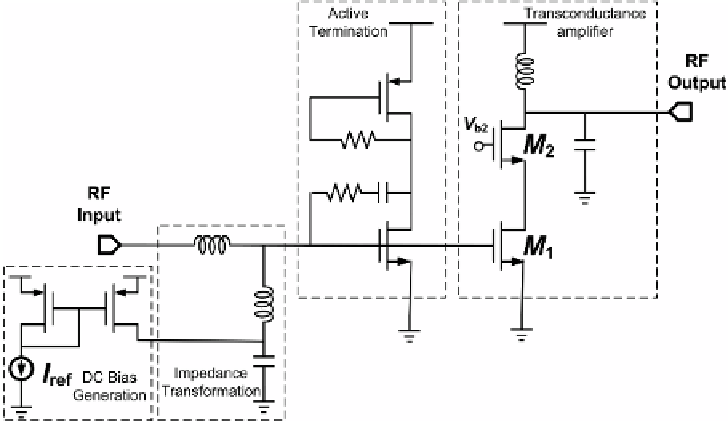
insight into circuit behavior. In this section, a low-noise-amplifier (LNA) circuit is
designed in a 0.13 μm CMOS process [8], the simplified circuit schematic of which is
shown in Fig.3.
In this example, we consider the transistors' driving strength (
tr_strengh
) as a main
source of process variations. Transistor strength describes the variations in the tran
sistor speed and the current. The data is provided by the foundry and it is set between
-3σ and +3σ. Additionally, temperature is considered as an environmental variation,
and it varies in the range of -20°C to 60°C. Two design parameters are considered.
One is reference current
I
ref
which is used to generate the input DC bias.
I
ref
is set in
the range of 50 μA to 200 μA. The other parameter is mlna which is the multiple of
the widths of the amplifier transistors M1and M2. mlna is in the range of 0.5 to
2. Here the performance of interest is the voltage gain at the center frequency
(
maxlnagain
)
.
Fig. 3.
Simplified low-noise-amplifier circuit schematic
The Kriging performance model
maxlnagain
(
tr_strength
,
T
,
mlna, I
ref
) was con-
structed using the data obtained from transistor-level simulations in HSPICE
®
. Latin
Hypercube sampling with corner points was used as the initial sampling strategy.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search