Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
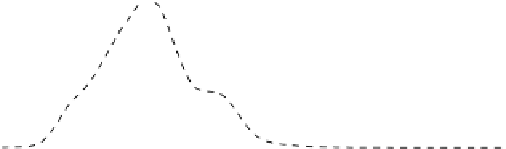
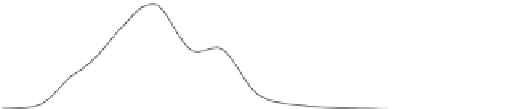
Fig. 2.
Responses as in Figure 1 for a different time interval using the basic surrogate formulation
(10) (top) and exploiting the modifications (13) of the response correction scheme (bottom)
large (possibly negative) correction factors
a
k
. While such a correction ensures zero-
order consistency at the point where it was established (i.e.,
u
k
), it may lead to (locally)
poor approximation in the vicinity of
u
k
.
Figures 2 and 3 (top) illustrate these issues by showing the smoothed surrogate's,
fine (down-sampled) and coarse model responses
β
f
and
y
c
for the state detritus
at one illustrative time interval and depth layer. Shown are the model responses at the
same points
s
k
,
y
u
k
and its neighborhood
u
k
∈ B
δ
(
u
k
)
as in Figure 1.
It should be pointed out that the overall shape of the surrogate's response still pro-
vides a reasonable approximation of the fine model one (and more accurate than the
corresponding coarse model response) despite of the distortion illustrated in Figures 2
and 3. This is supported by the fact that even without addressing these issues, the SBO
was able to yield satisfactory results, not only with respect to the quality of the final so-
lution, but, most importantly, in terms of the low computational cost of the optimization
process. This was already demonstrated in [14].
4.3
Improved Response Correction Scheme
The response distortion described in the previous section is problematic towards the
end of the surrogate-based optimization run when a higher accuracy of the surrogate is
required to locate the fine model optimum more accurately. The ”'spikes”' appearing
in the response due to large values of the correction term can be viewed, in a way, as
a numerical noise that slows down the algorithm convergence and makes the optimum
more difficult to locate.
A few simple means described below can address these issues and further improve
the accuracy of the surrogate's response as well as the performance of the optimiza-
tion algorithm. We introduce non-negative bounds for the coarse model response (the
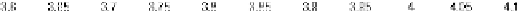






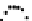











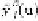
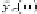

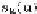
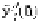









































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search