Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
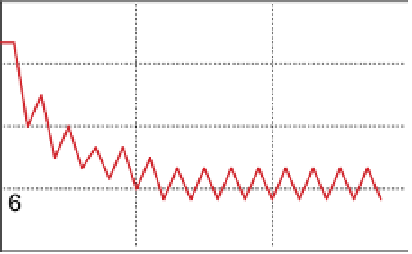
You can build a similar system using a label modifier instead (
Figure 6.18
). In this
case, the heater's output rate is adjusted by the actual temperature, creating a more
subtle temperature curve. This simulates a heater that can produce varying amounts
of heat rather than a fixed amount, as in Figure 6.17.
FIGURe 6.18
heater feedback
mechanism using a
label modifier
Feedback by Affecting Outputs
A feedback loop can also be created by a circuit of connections that affects the output
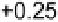
of an element. For example, consider a Machinations diagram for an air conditioner
(
Figure 6.19
). The higher the temperature, the faster the temperature is drained.
FIGURe 6.19
an air conditioner
in machinations
Any changes that affect the output of a node can also close a feedback loop. In this
case, output can be affected directly by a label modifier or by a trigger or activator
affecting an element at the end of the resource that is able to pull resources (such as
a drain, converter, or gate, as in
Figure 6.20
).
FIGURe 6.20
closing a feedback
loop by affecting
the output