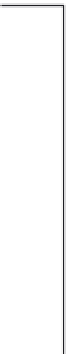Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Stratospheric
effects
Atmosphere
NO
x
Ozone
effects
PM and
visibility effects
GH
effects
Energy
production
N
2
O
Terrestrial
ecosystems
NO
x
NH
3
NH
x
Agroecosystem effects
Food
production
Forests and
grassland
Crop
Animal
Soil
Soil
People
(food; fiber)
N
org
NO
3
N
2
O
Groundwater
effects
Human activities
Surface water
effects
Coastal
effects
Ocean
effects
The Nitrogen
Cascade
Aquatic ecosystems
= Indicates denitrification potential
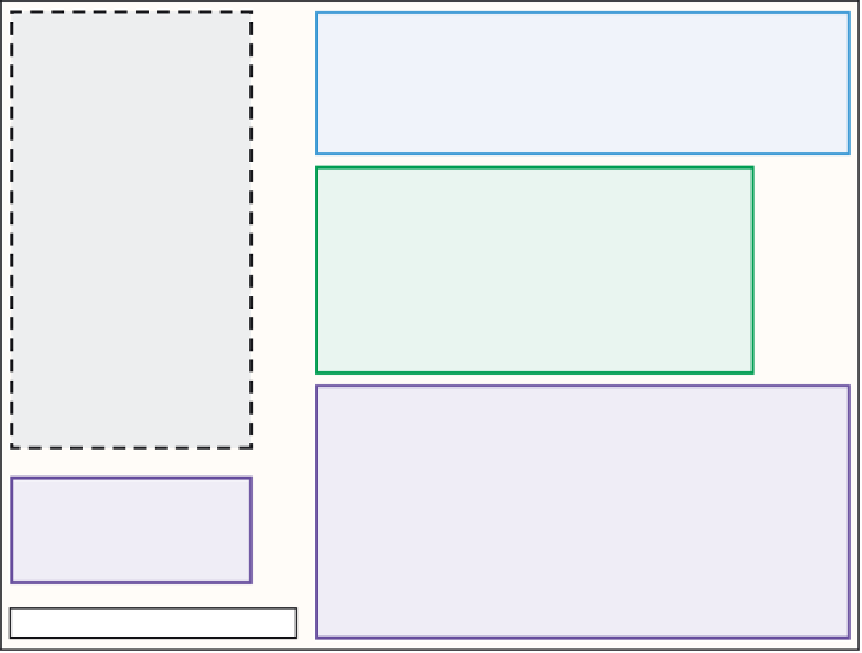
FIGURE 7.3
The nitrogen cascade. Nitrogen added to the environment by human activity “cascades” through
the atmosphere and terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems causing a series of air- and water-quality problems. (From
Galloway 2003.)
places, and (2) this extra N can be “too much of a good thing” and cause a wide variety of
environmental problems.
NITROGEN CYCLE PROCESSES
As stated earlier, the N cycle is one of the more complex nutrient cycles. In the following
sections we define and describe the controls on each of the processes shown in
Figure 7.4
.
Table 7.1
is a handy “cheat sheet” listing the dominant forms and processes of the N cycle.
Nitrogen Fixation
Pathways:
N
2
!
NH
3
N
2
!
various forms of reactive N in the atmosphere
ð
NO
y
Þ