Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
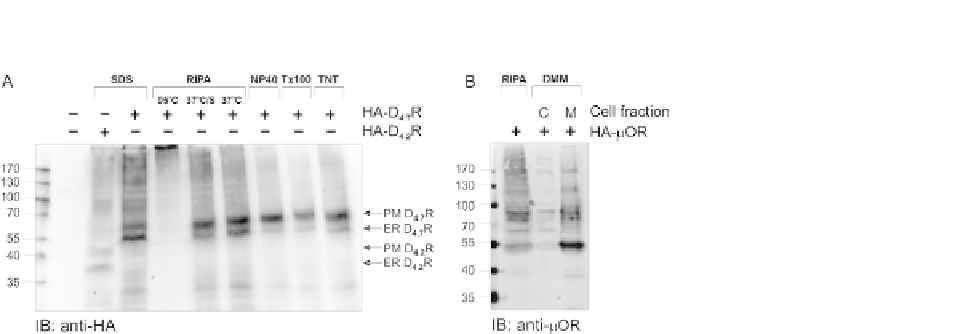
FIGURE 17.1
Comparison of different lysis methods. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with
pHA-D
4.7
R (additional control transfected with pHA-D
4.2
R was introduced to distinguish
bands of the right molecular level) to compare the efficiency of different lysis methods (SDS,
RIPA, NP-40, Triton X-100 (Tx100), and TNT lysis buffer). The lysates were denatured at
37
C in SDS sample buffer with addition of 50 mM DTT. For RIPA lysis also the influence of
sonication (S) and denaturation at two different temperatures (95 and 37
C) was tested. The
receptor was visualized by immunoblotting with mouse anti-HA (16B12) and antimouse
IRDye 800. PM-mature, fully glycosylated plasma membrane receptor; ER-ER-retained
receptor. (B) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with HA-m opioid receptor (mOR),
using Ca
3
(PO
4
)
2
method. Forty-eight hours after transfection cells were lysed with DMM
or RIPA lysis buffers to compare efficiency of these buffers. Samples were denatured with
SDS sample buffer and loaded on an SDS-PAGE gel. The protein was detected by
immunoblotting with rabbit anti-mOR antibody and antirabbit IRDye 800. C-cytoplasmic
proteins and M-membrane proteins.
can also be added to optimize the solubilization of the membrane proteins (
Holden &
Horton, 2009
).
Following incubation, the lysis solution is centrifuged at 8000
g
for 10 min,
resulting in a pellet and the supernatant, which contains the extracted membrane
proteins.
17.2.2.2.2
n-Dodecyl-b-
D
-maltoside (DDM) lysis
The pellet is resuspended in 0.5 ml buffer containing 20 mM Tris/HCl pH 8.0, 1 mM
EDTA, 0.35 mM NaCl, 0.5%
n
-dodecyl-
b
-
D
-maltoside (DMM), and inhibitors
(
Table 17.3
). Maltosides are a class of detergents often used for the solubilization
of membrane proteins (
Allen et al., 2009; Berger et al., 2005; Grisshammer,
2009
). After centrifugation at 20,000
g
for 10 min, the membrane proteins will
mainly be in the supernatant fraction.
This lysis method shows a better band separation and less smear formation com-
pared to the RIPA lysis, what can be observed in
Fig. 17.1
B. On top of this, there is no
addition of SDS or doc in this buffer, so there is no risk for denaturation resulting in
the loss of the interactions.