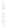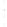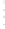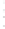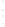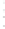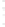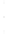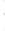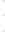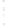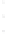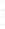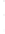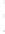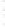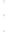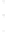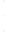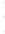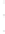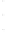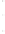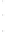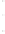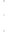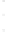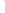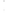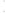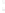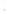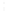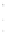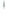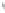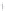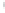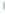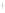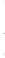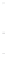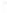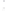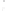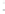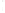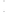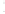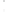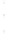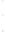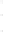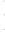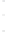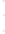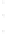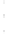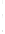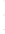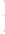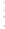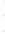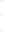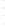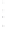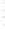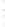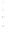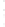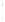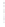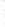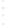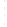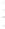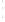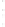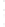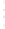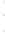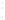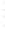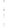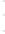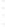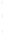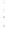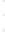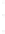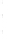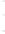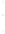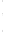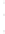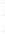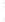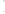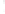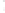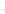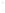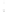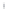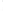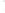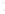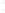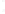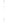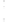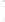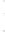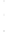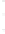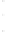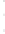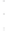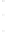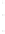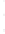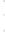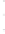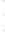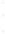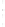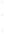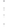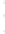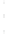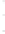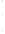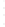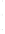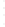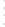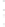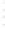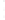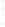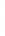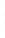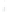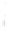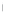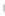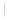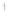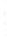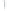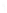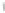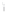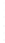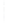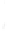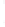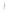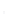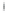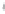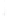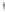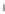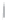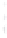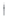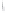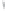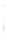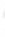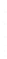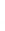Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Gaussian,
σ
= 1
Gaussian,
σ
= 1.2
0.2
0.2
0.15
0.15
0.1
0.1
0.05
0.05
0
0
5
5
5
5
0
0
0
0
y
−5
−5
y
−5
−5
x
x
(a)
(b)
Laplacian of Gaussian
Difference of Gaussians
0.01
0.01
−0.01
−0.01
−0.03
−0.03
−0.05
−0.05
5
5
5
5
0
0
0
0
y
y
−5
−5
−5
−5
x
x
(c)
(d)
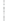
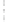
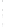
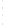
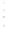
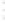
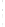
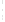
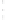
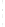
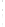
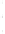
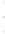
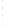
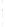
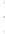
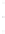
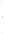
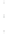
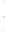
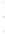
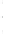
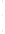
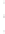
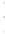
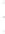
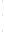
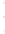
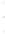
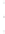
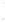
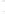
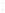
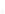
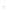
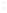
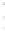
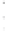
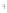
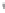
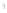
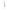
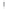
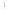
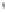
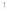
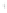
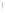
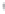
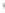
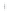
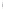
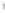
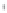
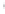
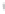
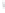
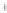
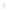
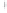
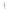
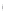
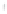
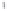
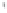
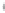
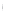
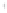
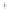
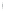
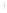
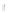
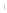
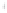
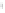
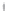
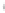
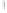
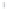
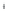
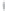
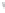
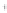
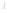
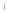
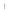
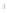
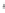
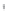
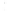
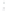
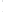
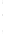
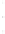
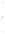
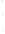
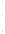
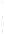
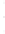
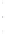
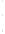
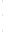
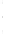
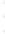
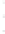
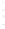
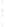
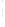
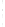
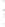
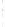
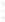
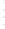
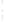
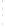
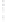
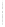
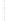
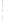
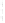
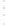
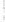
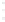
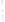
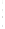
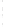
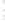
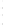
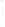
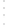
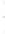
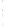
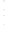
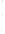
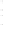
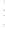
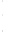
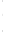
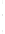
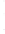
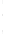
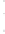
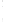
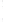
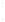
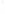
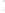
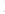
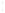
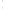
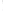
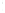
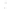
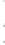
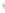
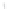
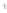
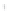
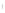
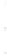
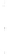
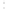
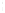
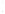
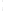
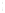
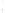
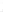
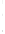
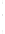
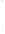
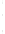
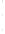
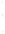
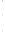
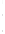
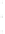
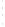
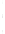
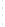
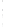
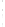
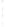
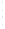
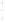
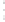
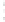
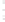
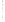
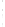
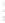
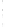
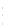
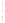
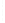
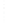
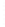
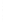
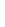
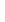
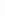
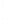
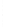
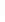
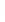
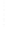
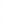
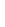
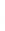
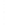
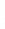
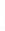
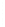
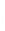
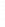
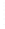
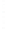
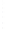
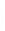
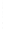
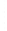
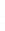
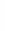
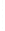
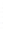
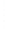
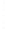
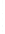
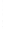
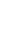
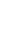
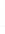
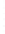
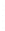
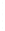
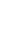
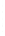
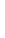
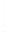
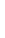
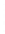
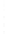
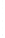
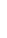
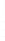
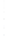
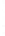
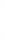
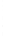
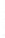
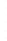
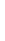
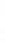
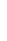
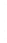
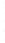
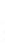
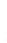
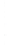
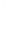
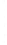
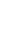
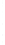
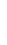
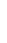
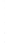
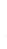
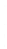
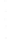
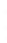
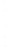
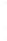
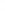
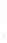
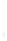
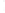
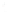
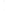
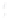
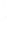
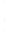
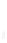
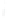
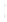
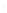
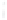
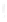
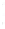
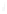
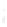
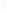
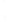
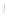
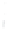
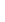
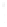
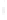
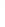
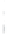
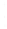
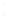
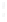
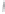
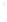
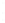
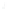
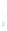
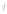
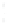
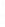
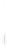
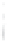
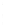
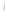
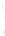
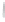
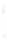
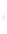
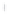
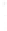
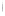
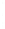
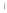
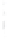
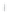
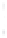
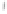
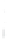
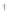
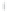
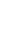
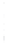
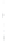
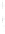
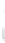
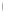
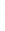
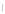
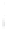
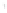
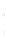
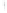
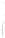
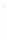
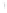
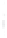
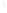
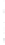
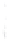
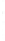
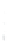
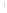
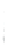
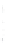
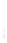
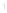
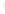
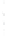
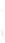
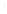
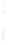
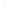
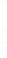
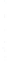
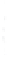
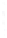
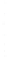
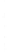
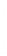
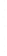
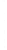
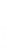
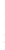
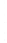
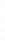
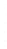
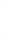
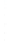
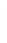
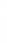
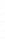
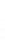
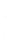
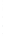
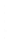
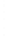
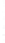
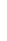
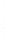
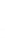
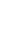
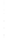
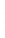
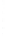
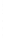
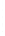
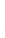
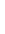
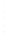
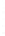
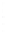
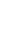
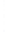
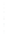
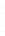
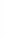
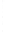
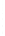
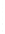
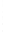
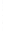
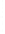
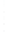
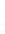
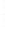
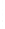
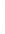
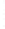
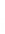
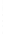
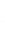
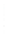
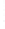
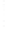
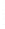
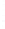
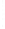
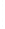
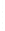
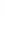
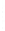
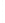
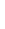
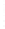
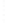
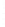
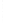
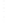
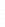
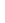
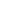
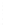
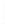
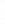
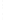
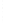
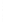
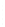
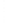
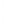
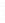
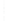
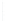
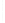
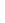
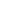
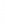
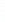
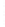
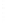
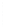
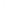
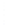
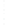
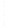
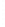
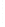
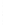
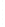
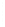
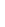
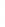
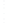
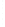
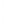
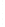
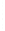
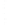
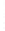
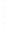
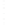
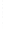
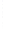
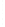
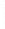
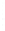
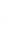
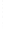
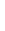
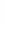
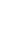
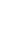
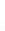
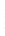
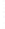
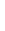
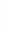
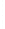
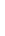
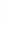
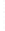
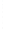
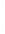
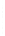
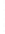
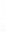
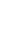
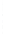
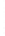
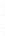
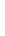
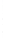
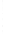
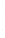
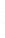
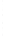
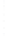
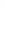
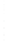
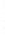
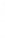
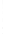
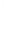
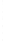
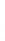
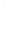
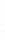
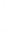
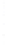
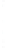
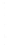
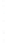
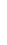
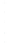
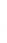
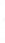
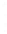
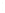
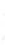
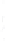
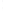
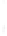
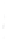
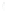
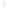
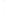
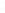
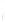
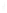
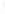
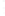
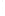
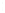
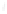
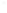
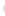
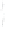
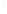
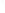
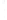
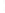
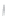
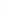
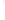
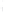
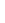
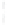
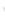
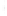
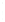
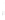
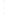
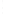
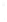
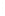
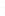
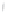
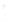
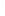
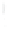
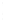
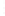
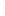
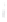
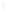
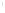
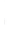
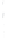
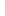
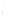
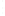
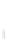
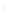
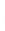
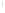
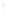
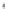
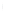
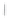
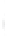
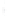
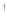
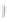
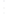
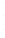
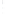
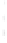
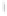
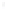
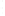
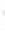
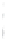
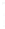
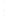
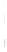
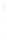
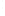
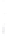
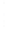
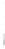
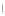
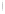
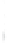
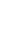
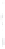
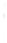
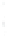
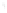
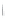
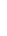
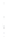
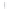
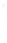
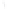
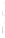
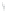
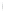
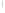
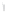
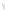
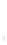
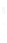
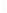
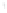
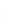
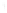
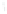
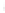
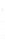
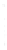
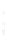
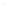
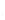
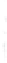
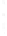
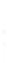
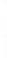
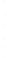
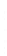
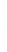
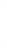
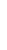
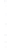
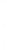
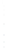
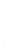
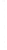
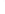
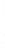
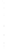
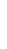
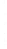
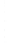
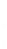
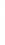
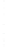
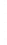
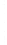
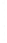
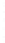
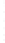
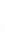
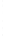
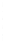
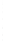
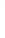
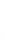
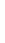
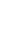
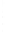
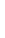
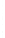
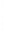
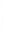
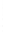
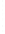
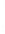
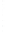
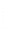
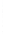
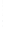
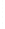
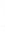
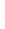
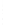
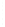
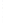
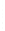
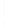
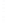
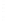
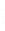
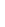
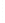
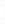
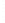
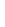
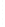
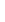
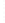
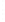
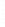
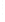
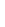
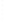
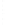
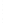
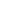
Figure 4.8.
(a) A Gaussian with
σ
= 1. (b) A Gaussian with
σ
= 1.2. (c) The Laplacian of Gaussian
with
σ
= 1. (d) The difference of the Gaussians in (b) and (a), normalized to have the same
maximum value as (c). We can see that the DoG is a good approximation to the LoG.
As with LoG detection, we seek maxima in both the spatial and scale dimensions to
detect features.
Lowe proposed a rearrangement of scale space to make the detection of local
maxima more computationally efficient. We define an
octave
of a Gaussian scale
space as a pair of images whose smoothing factors
idea was to define the constant factor
k
characterizing the scale space as
k
σ
2
s
,so
=
that each set of
s
1 images results in an octave. The image beginning each octave
is downsampled by a factor of 2 in both directions, but the sizes of the sequence
of Gaussian filters applied at each octave remains the same. In this way, we avoid
applying very large filters to original-sized images, and instead apply same-sized
filters to increasingly smaller images. If we just took the first image in each octave, we
would have a Gaussian pyramid, as discussed in Section
3.1.2
. Figure
4.9
illustrates
the idea. Lowe suggested using
s
+
=
3 intervals (that is, four images per octave), with a
base scale of
σ
=
1.6 applied to the first image in each octave (after downsampling).
0
8
While the word “octave” might imply a factor of eight is involved, the term originally comes from
music theory (i.e., there are eight notes in a major scale, which corresponds to a doubling of
frequency).