Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
2
=9
m=1,
s
1
2
=36
m=0,
s
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
1.5
1
0.5
-
-
-
0
w
0.5
1
1.5
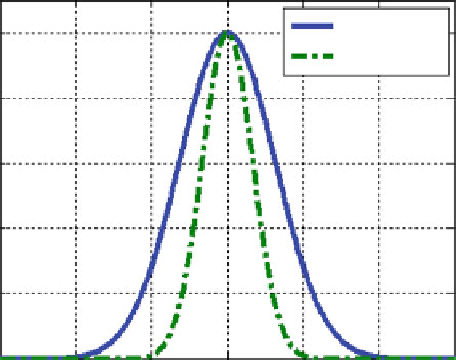
Fig. 4.16
Characteristic functions for normal variables
X
and
Y
(absolute values)
s
2
¼ s
1
þ s
2
:
m ¼ m
1
þ m
2
;
(4.104)
The characteristic function of the sum of independent variables is equal to the
product of the characteristic functions:
fðoÞ ¼ f
1
ðoÞf
2
ðoÞ:
(4.105)
The characteristic functions of the normal variables
X
i
,
i ¼
1, 2, according to
(
4.100
), is:
f
X
i
ðoÞ ¼
e
jom
i
o
2
s
i
2
;
i ¼
1
;
2
:
(4.106)
2
From (
4.103
) to (
4.106
) we have:
f
X
ðoÞ ¼
e
jom
1
o
2
s
1
2
2
e
jom
2
o
2
s
2
2
¼
e
joðm
1
þm
2
Þ
o
2
ð
s
1
2
þ
s
2
2
Þ
¼
e
jom
o
2
s
2
:
(4.107)
2
2
2
Comparing (
4.107
) with the expression for the characteristic function of a
normal variable (
4.100
), we can see that the expressions are equal, thus indicating
that
the sum of normal random variables is also a normal random variable.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search