Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
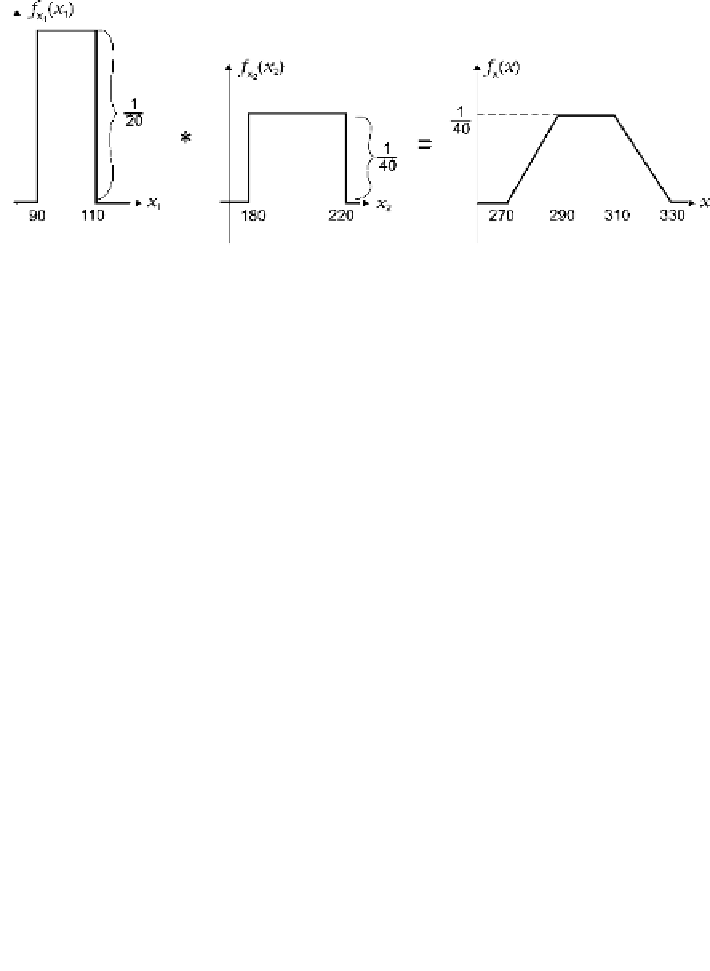
Fig. 3.26
Convolution of the uniform PDFs
Exercise 3.18
The random variables
X
1
and
X
2
are independent. Find the density of
their sum if the corresponding densities are given as:
f
X
1
ðx
1
Þ¼a
e
ax
1
uðx
1
Þ;
f
X
2
ðx
2
Þ¼b
e
bx
2
uðx
2
Þ;
(3.322)
where
a
and
b
are constants.
Solution
The density of the sum
X ¼ X
1
þ X
2
(3.323)
is equal to the convolution of the densities (
3.322
):
f
X
ðxÞ¼f
X
1
ðx
1
Þf
X
2
ðx
2
Þ:
(3.324)
For
x <
0,
f
X
ðxÞ¼
0
:
(3.325)
For
x >
0,
1
f
X
ðxÞ¼
f
X
1
ðx
1
Þf
X
2
ðx x
1
Þ
d
x
1
1
¼ ab
1
ab
a b
e
ax
e
ax
1
e
bðxx
1
Þ
d
x
1
¼
:
(3.326)
x
Exercise 3.19
Find the characteristic function of the variable
X
with the density
function shown in Fig.
3.27
in terms of the characteristic function of the variables
X
1
and
X
2
. The variable
X
is the sum of
X
1
and
X
2
, and the variables
X
1
and
X
2
are
independent.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search