Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
However, the r.v.
X
is less than 3 if it is equal to either
1 or 2, resulting in:
PfX <
3
g¼
0
:
25
þ
0
:
25
¼
0
:
5
:
(2.460)
This probability corresponds to the value of the distribution in the distribution
plot for
x ¼
3 and to the area below delta functions from
1
until 3 in the PDF
plot, i.e., again equal to 0.5.
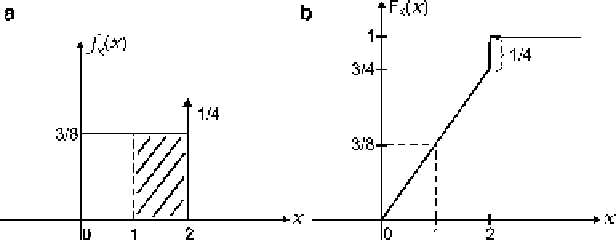
Exercise E.2.5
The PDF of the random variable
X
is given in Fig.
2.59a
. Find the
type of the random variable and plot the corresponding distribution function. Find
the probability that the random variable is equal to 1 and to 2, as well. Additionally,
find the probability that the random variable is greater than 1.
Answer
The random variable is mixed (i.e., it is continuous in the interval [0, 2]
and has one discrete value
X ¼
2, indicated by the delta function in point 2 of the
PDF plot). The corresponding distribution function is the integral of the PDF, as
demonstrated in Fig.
2.59b
.
The r.v is continuous in the interval [0, 2] and thus it does not take any particular
value in this interval, resulting in:
PfX ¼
1
g¼
0
:
(2.461)
However, the random variable takes the discrete value 2 with the probability
equal to 1/4
PfX ¼
2
g¼
1
=
4
:
(2.462)
Similarly, we have:
ð
2
3
8
þ
1
4
¼
5
8
:
PfX>
1
g¼
f
X
ðxÞ
d
x ¼
(2.463)
1
Fig. 2.59
(
a
) PDF and (
b
) distribution of the mixed random variable
Search WWH ::

Custom Search