Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
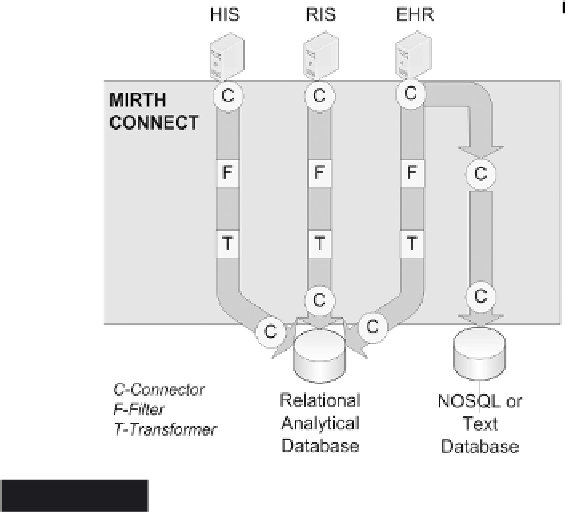
Mirth Connect showing the channels from the data
sources to the databases. Note that channels can
connect to other channels. In the example, the EHR
connection is split such that both fi ltered/transformed
and raw data can be inserted into independent data
stores
Figure 20.4
to each. Filters are broken up into a set of rules, which are connected
to each other by boolean operators. Rules can be written either using
a Rule Builder or by executing a small Javascript for more complex
rules.
Mirth uses a facility's own sample messages to assist in building
fi lters and transformations. Once a sample message is loaded either from
a fi le or by pasting it into the window, as shown in Figure 20.5, a message
tree is built with the message hierarchy from the data type based on
the sample data. This message tree is shown in Figure 20.6. Implementers
can then drag the data from this tree into either the Rule Builder or
Javascript, and Mirth will translate it into the correct variable from
the message.
Transformers have a similar interface to fi lters. Like the fi lters, the
sample input and output messages create a message tree that is used to
build a list of transformer steps. There are a couple of different options



Search WWH ::

Custom Search