Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
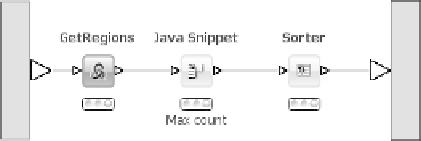
Figure 6.17
Identifi cation of regions of interest
the maximum count value from the count string whereupon all rows are
sorted by that value to retrieve the regions with the highest coverage as
the top entries in the output table.
Further open source tools for genomic data analysis are described in
Chapter 8 by Tsirigos and co-authors.
6.5 Conclusion and outlook
It is possible to perform sophisticated data analysis tasks in KNIME
using completely free software. The many contributors from the KNIME
community ensure that the number of freely available extensions will
continue to grow in the future, providing even more application areas
in which KNIME can be used at no cost. There are, naturally, some
areas in which no free methods are available and situations where
guaranteed support is necessary when reliability is crucial for the success
of projects. This is where commercial vendors come into play. KNIME's
modularity and licensing model facilitates the usage of a mixture of
free and non-free components. Another important aspect is the existence
of the KNIME.com company which not only sells training courses,
provides professional support, and develops enterprise extensions but
also plays a key role in the further development of KNIME's free open
source core.
6.6 Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the authors of the extensions described here
for making their nodes available to KNIME. Special acknowledgments
also go to Greg Landrum, Dmitry Pavlov, Frank Schaffer, and Martin
Horn for providing some of the example workfl ows shown in this
chapter.




Search WWH ::

Custom Search