Databases Reference
In-Depth Information
in the size of
p
, and exponential in the size of
k
. This makes it possible to
compute the optimal perimeter, as a reference value for the evaluation of
Γ
I
-
unsafe algorithms, for quite large values of
p
and practically relevant values
of
k
.
2.5
intervalCloaking
casper
nnASR
optimalUnsafe
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
4
6
8
10
12
14
k
(a) Area.
5
intervalCloaking
casper
nnASR
optimalUnsafe
4
3
2
1
0
4
6
8
10
12
14
k
(b) Perimeter.
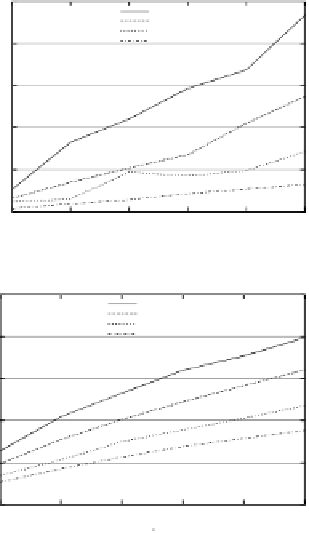
Fig. 6.
Area and perimeter as computed by
C
I
-unsafe algorithms with
p
= 100
,
000
and
k ≤
14.
Figures 6(a) and 6(b) show the average area and perimeter, respectively, of
four
C
I
-unsafe algorithms. Since the experimental results for the
nnALG
and
nnASR
algorithms are almost identical, in this section we report the results
of the
nnASR
algorithm only. The principle behind the
nnASR
algorithm
may induce the reader to think that the resulting region is minimal. Our
empirical results show that that this is not the case. On average,
nnASR
returns regions having a perimeter 30% larger than the one of the region
returned by
optimalUnsafe
. We also computed the average number of times
in which
nnASR
returns the same result as
optimalUnsafe
. We noticed that
this value rapidly decreases with the growing of
k
. For example, with
k
=4
and
p
= 100
,
000,
nnASR
returns the region with the minimal perimeter in
about 13% of the cases, while the percentage drops below 1% for
k
=14and